Non-gynaecological Cytology
Thyroid cytology
Follicular carcinoma
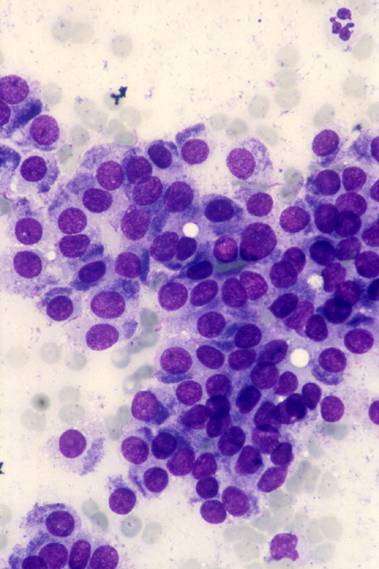
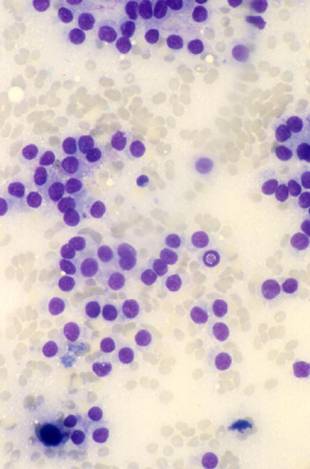
It represents the second most common thyroid cancer (5-15% of thyroid malignancies). It is usually a solitary nodule but, differently from follicular adenoma, it shows capsular infiltration and vascular invasion. Follicular carcinoma is usually divided into two histological subtypes: a minimally invasive with a very good prognosis and a widely invasive with poor prognosis, which tends to metastatize to lung and bones.
The cells of follicular carcinoma never show the nuclear features of papillary carcinoma, which helps to distinguish follicular carcinoma from the follicular variant of papillary carcinoma.
An MGG stain of an FNA from a follicular carcinoma. Groups of thyrocytes from a follicular carcinoma.