Non-gynaecological Cytology
Thyroid cytology
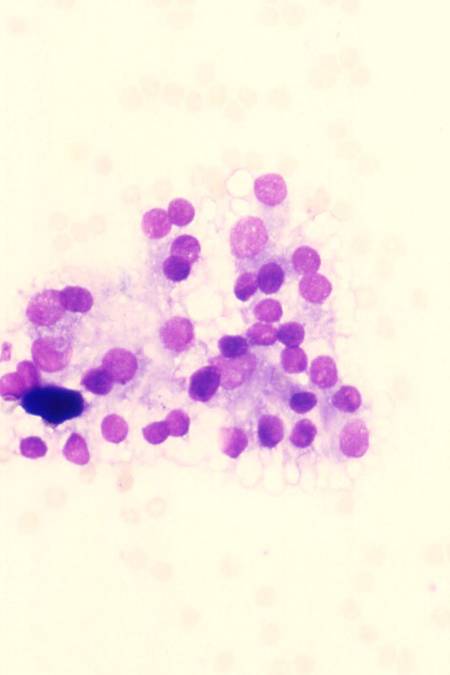
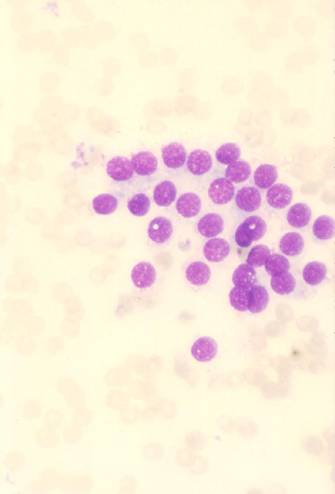
Follicular adenoma
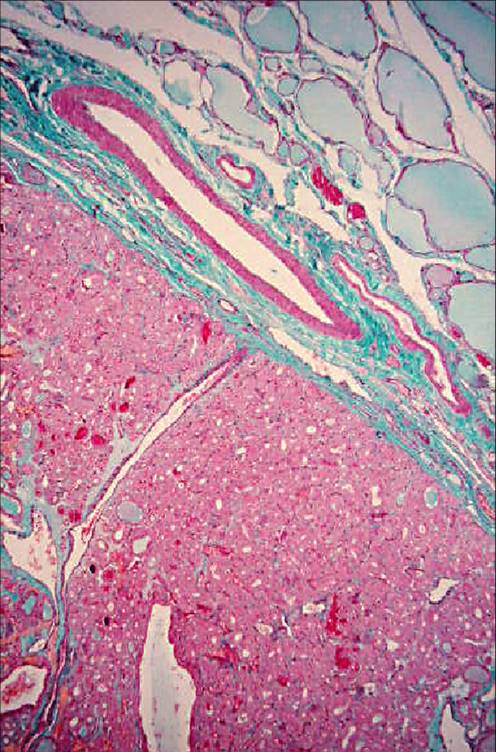
It is a benign neoplasm, presenting as a single nodule, usually not greater than 3 cm in diameter. Some of them can produce thyroid hormones and consequently cause hyperthyroidism (functioning or 'hot' adenomas). The hystologic pattern may vary: macrofollicular (composed of large follicles filled with colloid), microfollicular (with smaller follicles), trabecular (with follicular cells arranged in ribbons).
Classification (no prognostic significance)
- simple
- microfollicular
- trabecular
- oxyphil
- atypical
- papillary
- signet ring cell
Nodular hyperplasia Follicular neoplasia multiple solitary poorly encapsulated encapsulated architectural heterogeneity uniformity of the architecture cytologic heterogeneity cytologic homogeneity comparable areas in adjacent gland different from surrounding gland no compression of surrounding gland compression of surrounding gland
Microfollicular adenoma (histology)