Cervical Cytology
Quality assurance
Comparison of adequate smears against inadequate smears:
Satisfactory for evaluation Unsatisfactory for evaluation Appropriate labeling Lack of patient data Well displayed and well preserved squamous epithelial cells covering more than 10% of the area under the cover slip. Scant squamous epithelial cells component : less than 10% of the slide surface Presence of endocervical and or immature metaplastic cells Obscuring blood, inflammatory cells, excessive cytolysis, thick areas, poor fixation, air drying Clinical information provided –age, menstrual status, appearance of cervix , irregular bleeding e.g. post coital or post menopausal bleeding. Contaminants which obscure more than 50% of epithelial cells A SLIDE CONTAINING ABNORMAL CELLS SHOULD NEVER BE CLASSIFIED AS INADEQUATE.
Here are some examples of inadequate smears: Click on them to view the full picture
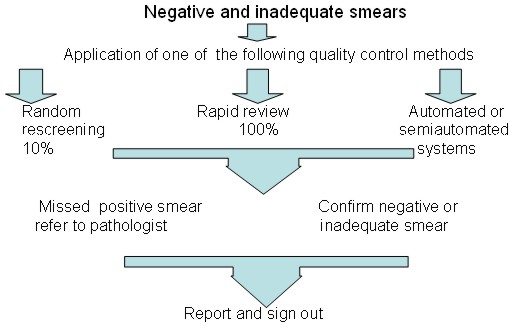
Quality control measures to reduce the risk of false negative smears
- Random re-screening: This method is widely used in the United States. It involves supervisory staff re-screening 10% of all smears classified as negative or inadequate by the primary screener. The whole slide should be examined allowing approximately 6 minutes per smear. Although the chances of detecting error are small, this approach increases awareness of risk of error.
- Rapid re-screening: This method is widely used in the UK. It involves supervisory staff performing a partial review of every slide classified as negative or inadequate by the primary screener. The slide is reviewed for 1 minute at low magnification (x10 objective) A record of the relative sensitivity of primary screening should be kept using the following formula:
_______________________________________
total abnormal smears after rapid review x 100
Flow chart to show quality control check of negative and inadequate smears after primary screening. Internal quality control procedures which should be applied periodically
- Peer review and regular discussion of abnormal smears
- Comparison of biopsy with cytology
- Review smear history of women with invasive cancer for possible false negative smear reports Slides should be stored for up to 10 years for this purpose
- Check on Workload and Monitoring turnaround time.
- Statistical monitoring of laboratory performance at regional or national level.