Cervical Cytology
Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) invasive squamous carcinoma of the cervix, and atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance (ASCUS)
| Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia(CIN) |
| Invasive Squamous Carcinoma |
| Atypical squamous epithelial cells of uncertain significance (ASCUS) |
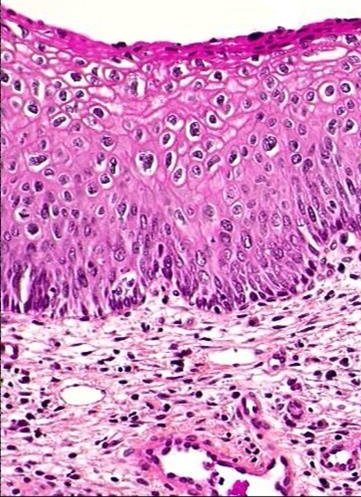
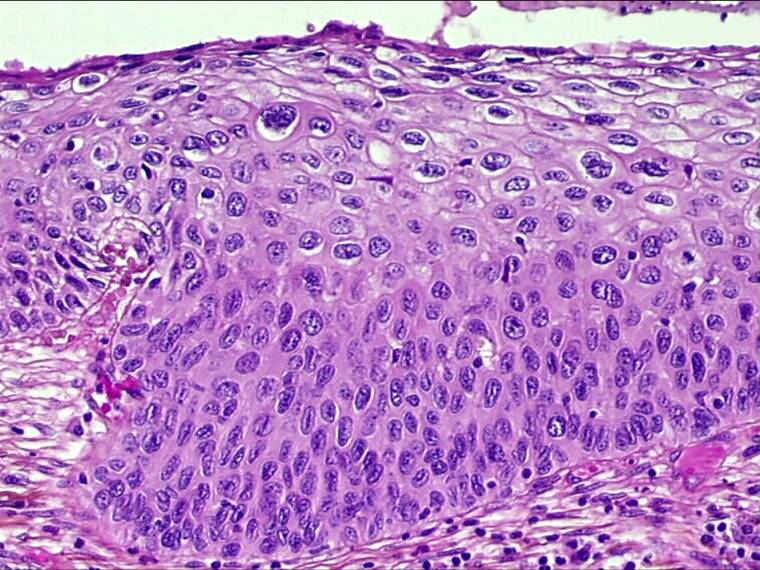
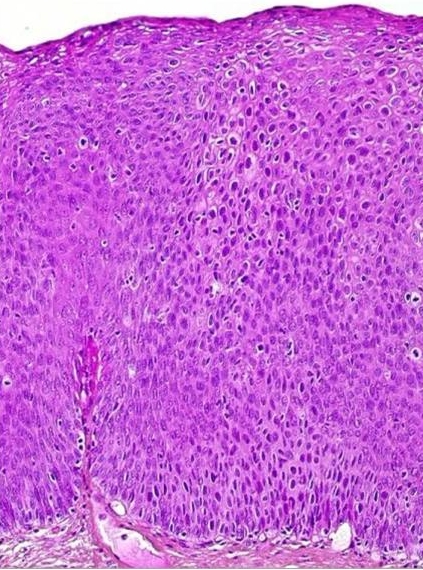
Morphological & biological characteristics of CIN
The abnormal cells found in the smear are derived from the surface of the CIN lesion. The abnormal cells appear singly or in streaks or in sheets. They can be distinguished from normal cells by the following features:
The morphology of cells from a focus of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia as they appear in cervical smears
- Disproportionate nuclear enlargement resulting in alteration of normal nuclear/cytoplasmic ratio.
- variation in nuclear size and shape.
- irregularity of nuclear outline
- hyperchromasia of nucleus and abnormal chromatin pattern
- large irregular and sometimes multiple nuclei (not in CIN1)
- The grade of CIN (CIN 1, 2 or 3) can be deduced from the degree of nuclear enlargement and alteration of n/c ratio.
The three enlargeable tables below describe and illustrate with library of slides the cytological features of the different grades of CIN