Specific infections of the cervix
The inflammatory changes described above are common to almost all cases of acute cervicitis. In some cases the actual microbiological organism can be identified in the smear or may produce a distinctive cytopathic effect permitting a diagnosis of specific infection.
A list of specific infections that can be identified by cytology is given below :
- Trichomonas vaginalis
- Candida sp
- Herpes genitalis
- Human Papillomavirus
- Actinomyces sp
- Chlamydia trachomatis
- Parasitic infection with Schistosoma haematobium , S. mansoni and Fliaria bancrofti can be detected in cervical smears. Granulomatous lesions suggestive of tuberculosis and cytomegalic inclusions have also been described.
 |
 |
 |
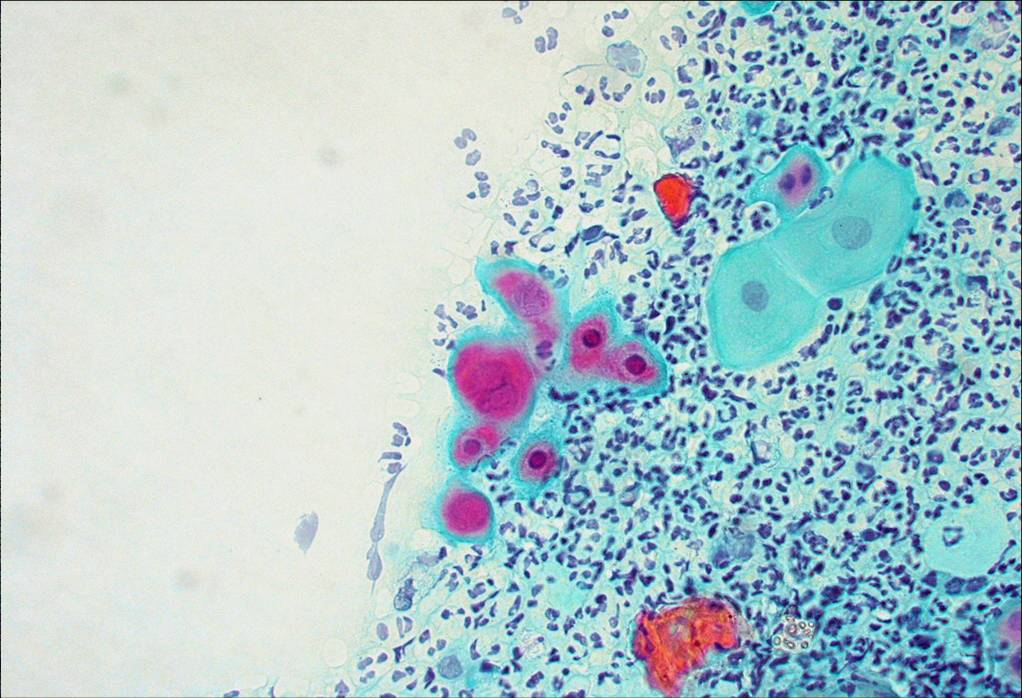
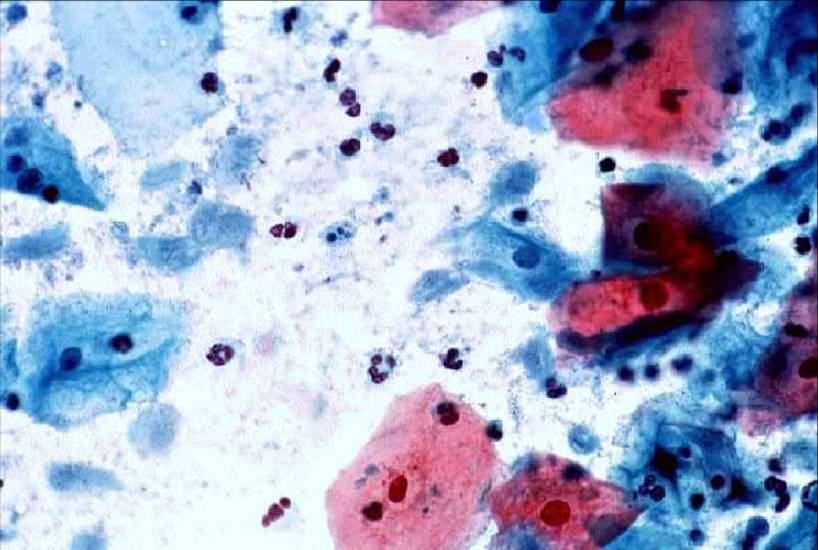
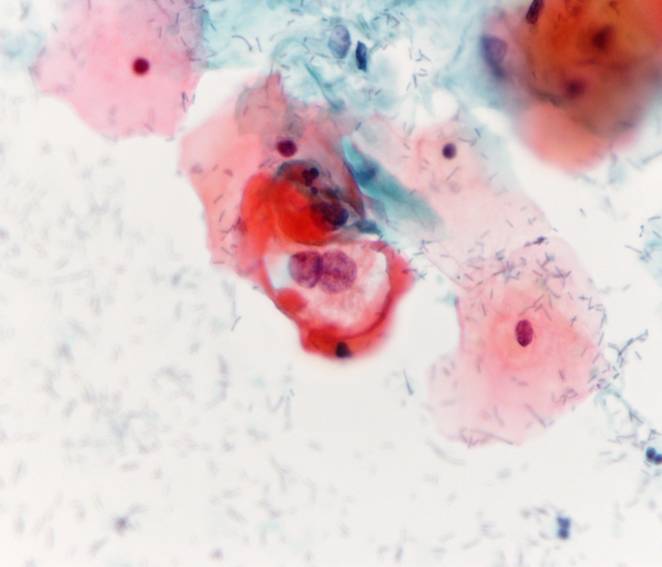
Trichomonas vaginalis |
Trichomonas vaginalis |
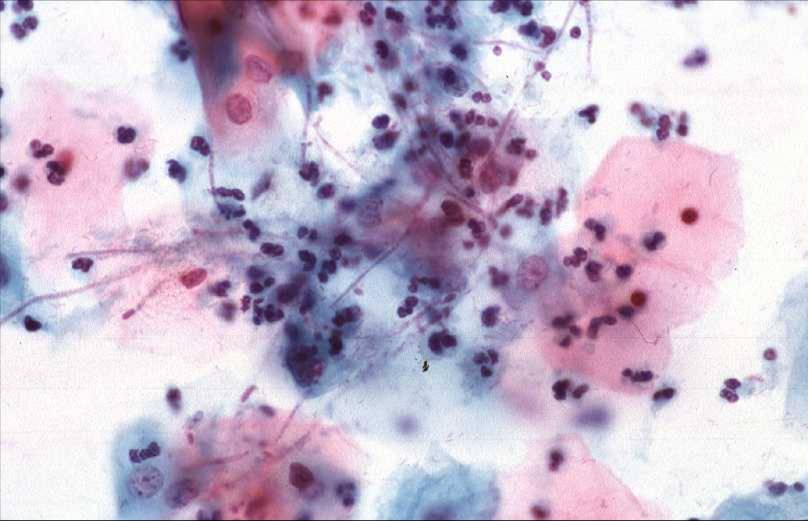
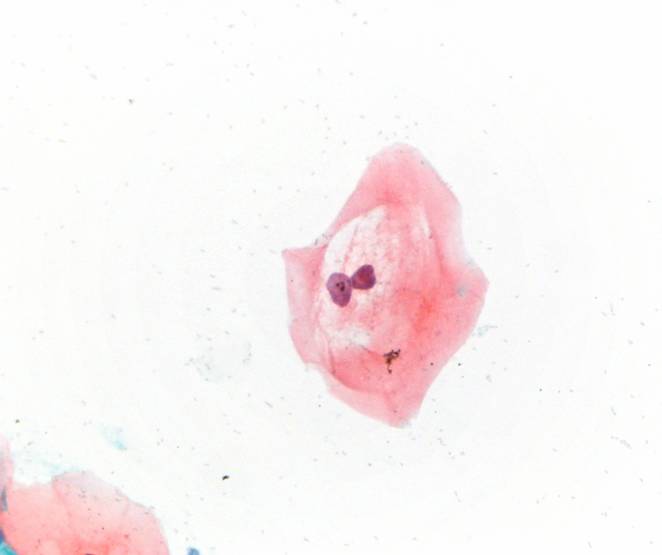
Candida species |
 |
 |
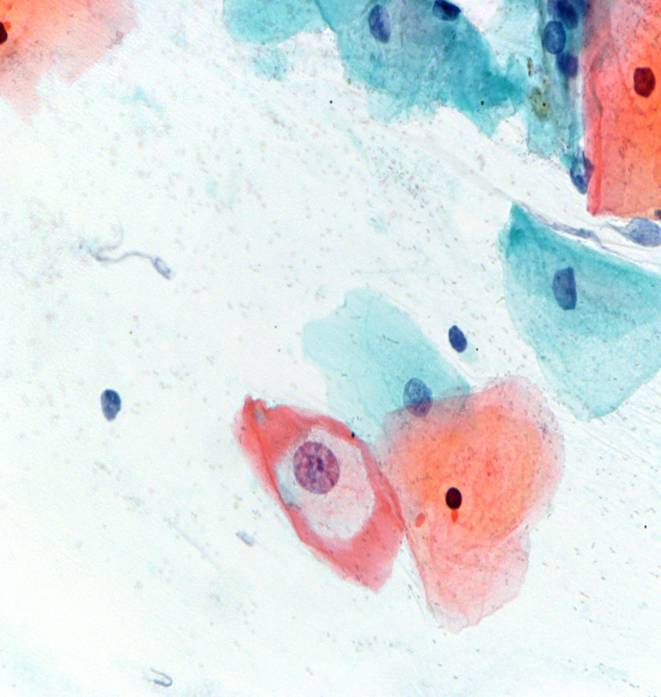 |
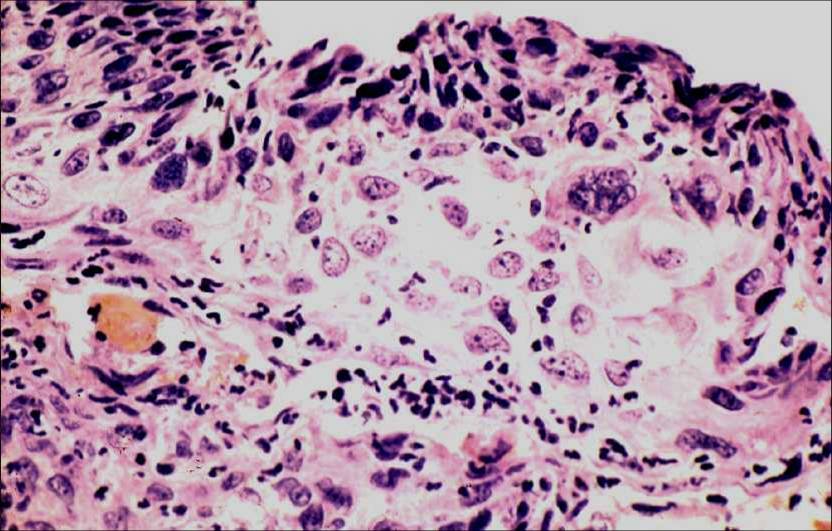
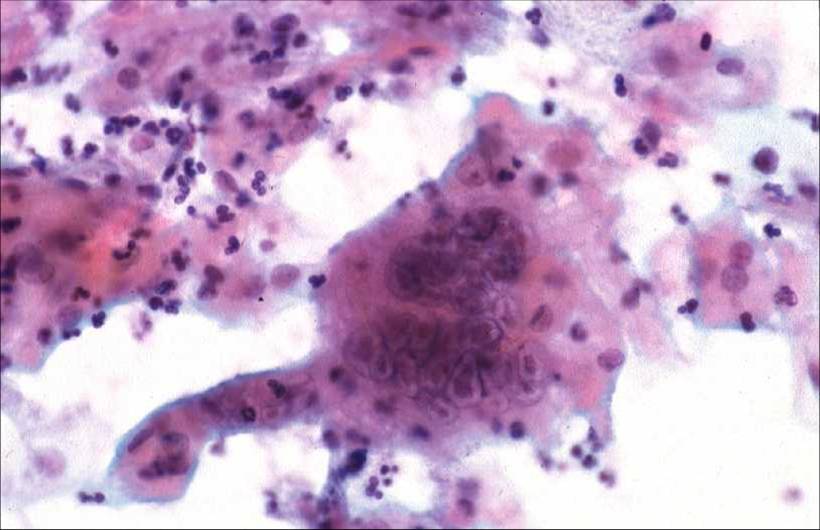
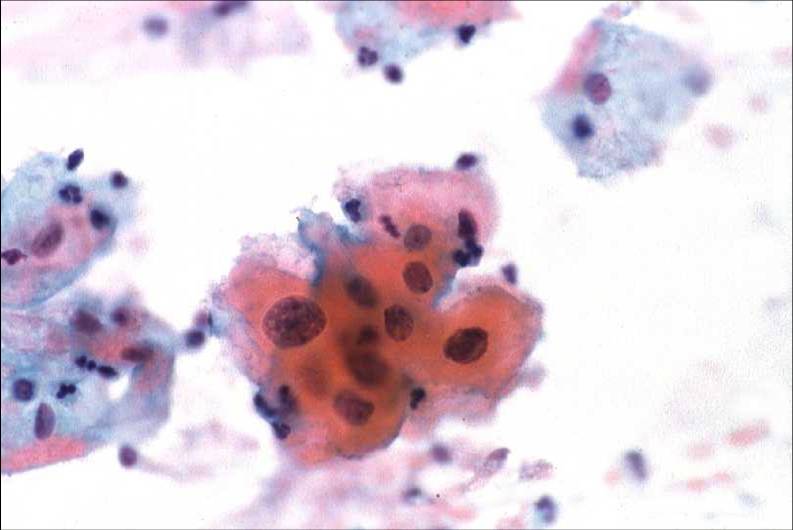
Human Papillomavirus infection |
Human Papillomavirus infection |
Human Papillomavirus infection |
 |
 |
 |
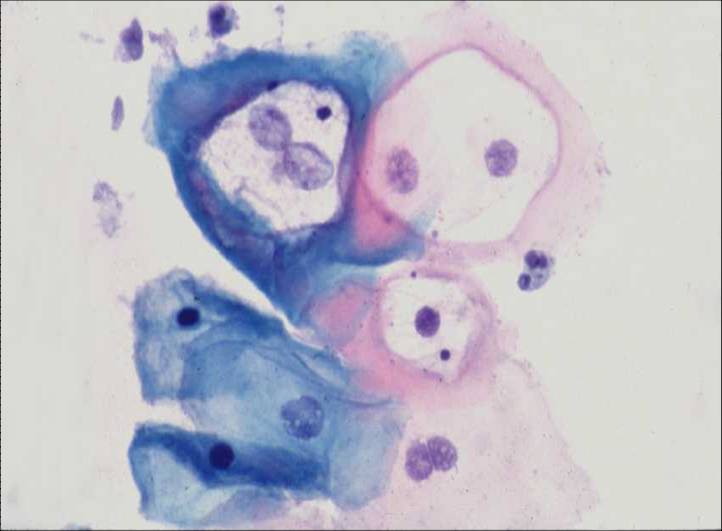
Human Papillomavirus infection |
Human Papillomavirus infection |
Human Papillomavirus infection |
 |
 |
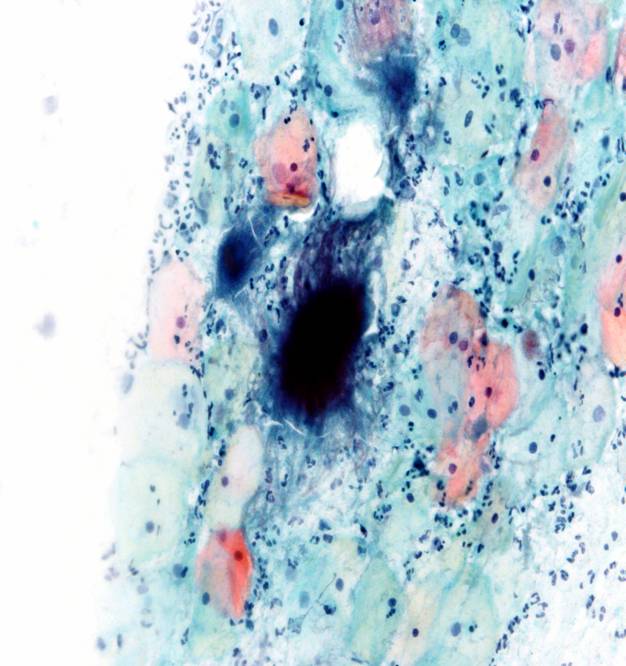 |
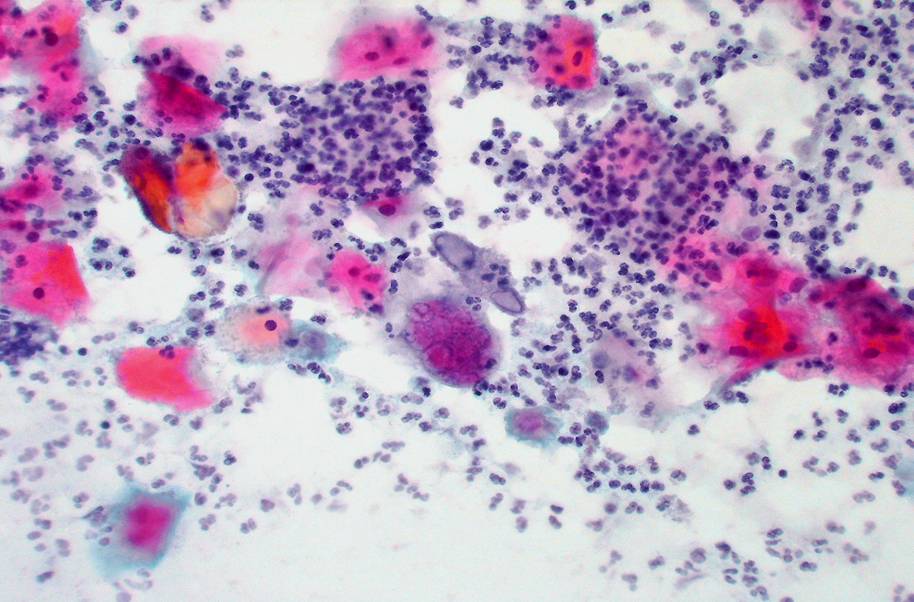
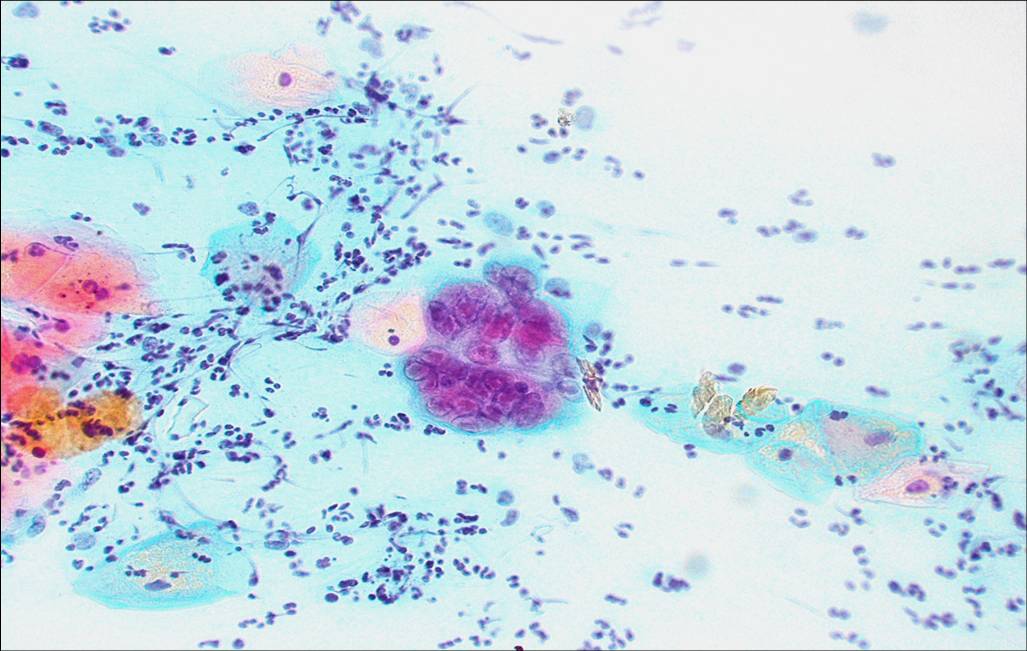
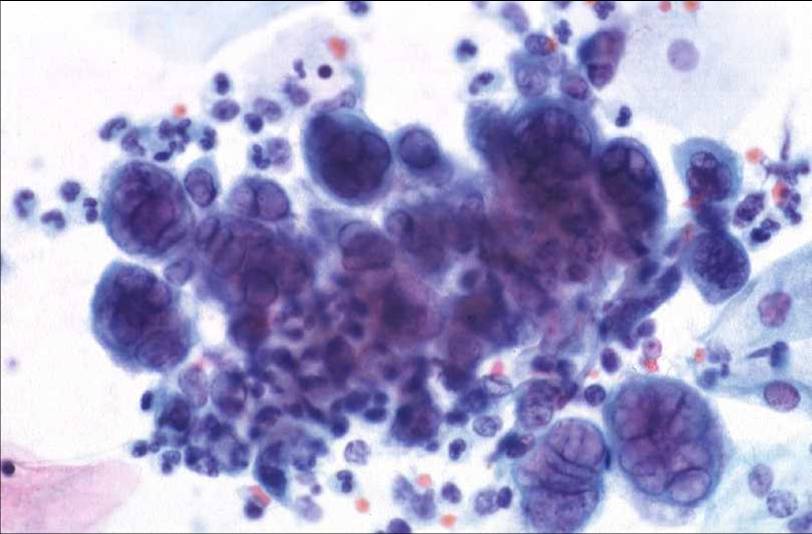
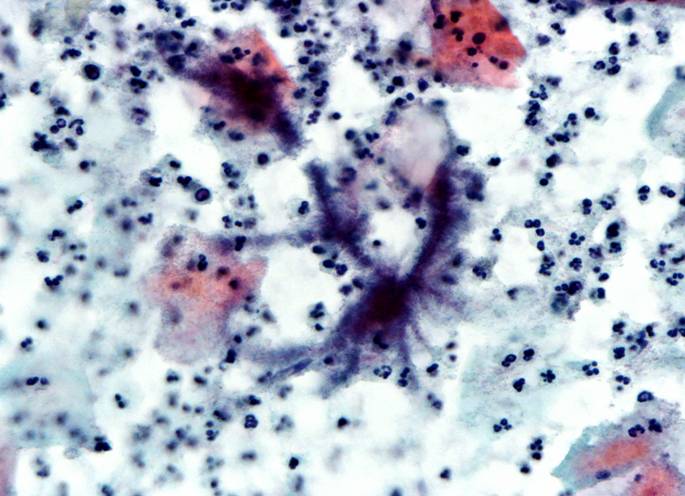
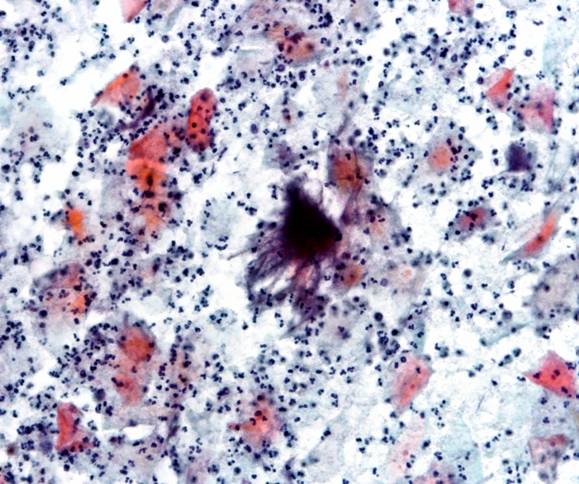
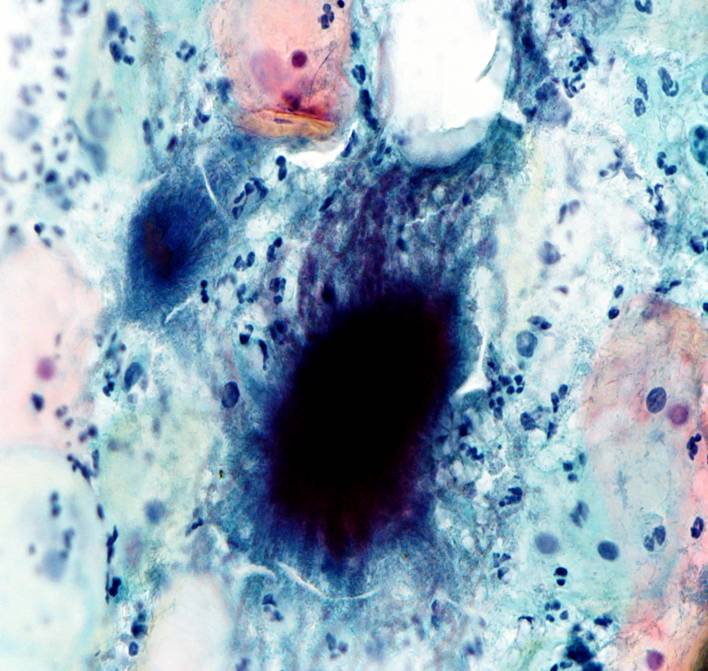
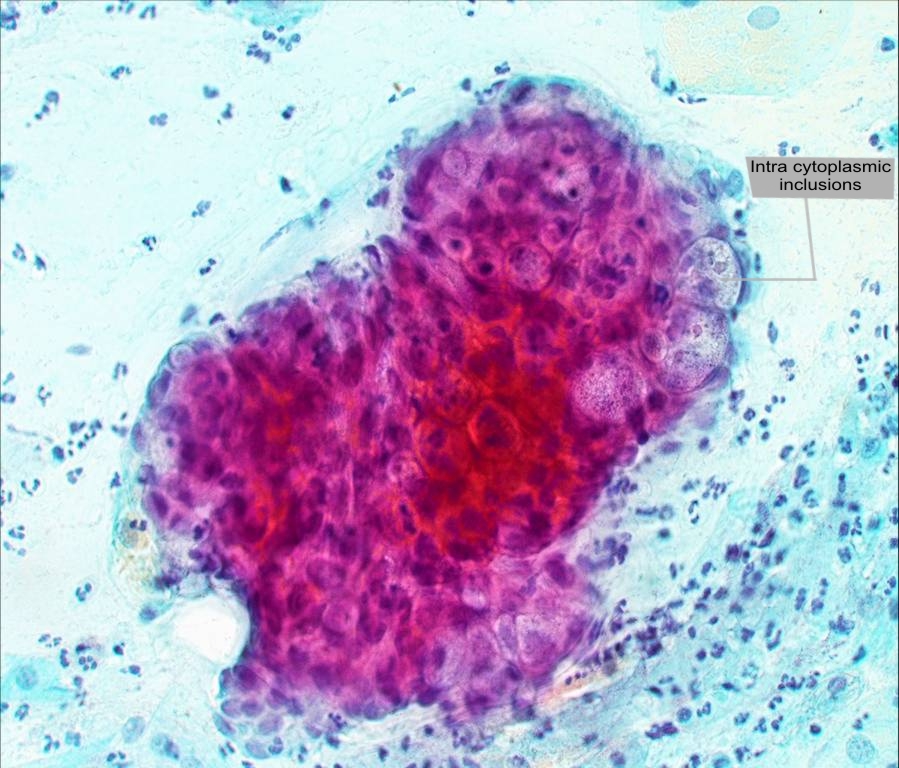
Actinomyces species |
Actinomyces species |
Actinomyces species |
 |
 |
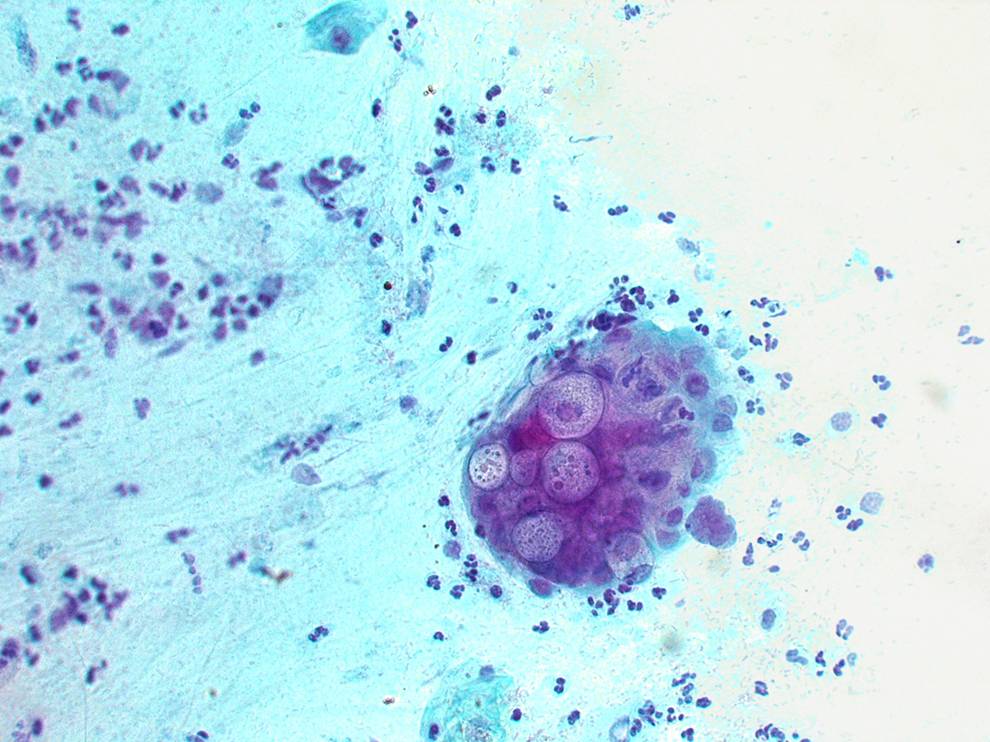 |
Actinomyces species |
Chlamidia trachomatis |
Chlamidia trachomatis |