| The Pap Test |
| Collection of specimens |
| Guidelines on laboratory organisation, processing and screening |
| Terminology and reporting |
Collection of specimens
Specimens can be obtained in three ways
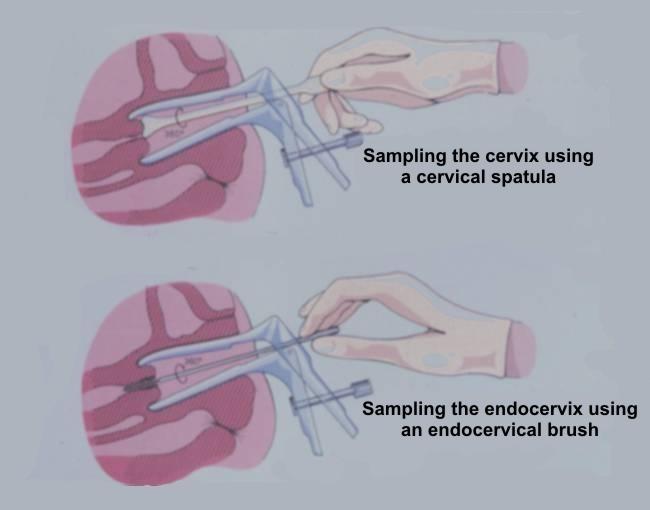
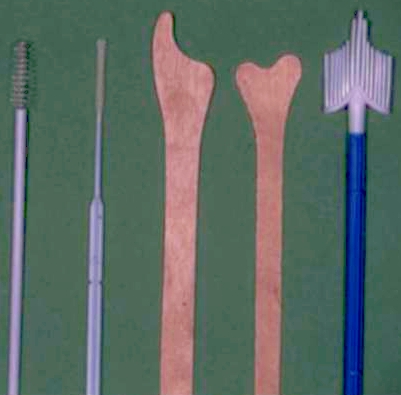
- Scraping the ectocervix with with a modified spatula (the Ayre spatula or a variation of it). This is the most widely used method in Europe for obtaining material for preparing conventional cervical smears
- Using an endocervical brush to sample the endocervix..
- Using a broom like device which samples both endo and ectocervix. These can be used for preparing conventional smear. Some devices have been modified for the preparation of liquid based cytology (LBC) specimens
The following steps are essential to ensure the Pap test is performed correctly
- A speculum must be inserted into vagina and the cervix clearly visualised.The cervical os should be located.
- The sampling device(s) used should be selected according to the shape and size of the cervix and the location of the squamocolumnar junction. An Ayre spatula is suitable for sampling the cervix in a parous woman ; however a spatula and brush may be needed in a post menopausal woman where the squamocolumnar junction lies within the endocervical canal.
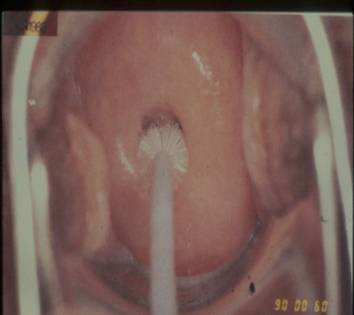
- The pointed end of the spatula should be inserted into the cervical os in a nulliparous cervix and the rounded end of the spatula inserted into the patulous os of a parous woman. The device should be rotated 360 degrees to remove the cells from the region of the transformation zone, squamocolumnar junction and endocervical canal.
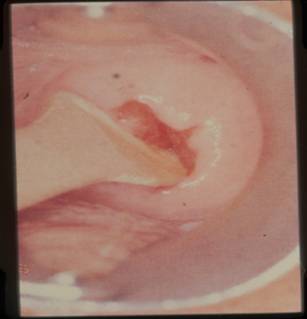
- The material on the spatula or brush must be transferred immediately to a glass slide which has been previously labeled with the patient’s name and date of birth.
- The glass slide must be fixed immediately with an appropriate fixative (95%alcohol) and the slides transported to the cytology laboratory in a container for processing together with the corresponding cytology request form.
- Samples taken for Liquid Based Cytology should be processed strictly in accordance with the manufacturers instructions. After sampling the cervix, the tip of the sampling device should be broken off into the transport medium in the container provided which should then be transported to the laboratory for processing if the Surepath method is being used. However if the Thinprep method is being used it is of the upmost importance that the tip of the sampling device is not included in the container
- A detailed description of cervical sampling can be found in Training package 3 (CYTOTRAIN PROGRAMME :The Pap Test Procedures)
Sampling the cervix using an endocervical brush Sampling the cervix. Note pointed end of spatula in cervical os An Ayre and an Aylesbury spatula
Preparation of a cervical smear. Note coplin jar containing fixative is immediately to hand to prevent air drying A range of smear taking devices: Endocervical brushes, wooden spatulae, and broom
Fixation of Pap smears
Proper fixation is an essential step in the preparation of cervical smears. It ensures that the cells are well stained and clearly displayed for microscopic analysis and preserved for immediate and future review. Fixation can be achieved by complete immersion of the slide in one of alcohol fixatives listed below for 15-20 minutes after which the slide can be removed from the fixative and transported to the laboratory for staining. Alternatively,fixation can also be achieved by spray fixation. Spray fixative consist of an alcohol base and carbowax that provides a thin protective waxy coat over the slide. The carbowax must be removed by immersion in alcohol before staining
A satisfactory fixative has to meet several requirements.
1. It should penetrate the cell rapidly so that detailed cell morphology is maintained.
2. Cell shrinkage should be minimal and uniform so that morphological distortions do not occur .
3. It should allow permeability of dyes across the cell boundaries and appropriate for the staining method used
4. It should permit cell adhesion to the glass microscope slide
5. It should be bactericidal, non toxic and permanent..The following fixatives are suitable for the fixation of cervical smears which are to be stained by the Papanicolaou method.
- 95% ethanol (for optimal fixation)
- 80% isopropanol
- 95% denatured alcohol (90 parts 95% ehanol, five parts absolute methanol and five parts absolute isopropanol)
- Reagent grade alcohol (absolute methanol, 80%isopropanol,90% acetone)
Fixation must be immediate . The smear must not be allowed to dry before fixation