Lymphoma
Primary thyroid non-Hodgkin lymphoma (PTNHL) is a rare neoplasm, which typically occurs in older-aged women in the setting of Hashimoto`s thyroiditis. The risk for a patient with thyroditis is much greater than in the general population, but occurrence of a lymphoma is very rare. Most patients present with an enlarging neck mass and cervical lymph nodes can be involved.
The three common types of PTNHL are: marginal zone B-cell lymphoma of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) type (MZL); diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBL); mixed MZL-DLBL type.
Cytologic diagnostic features
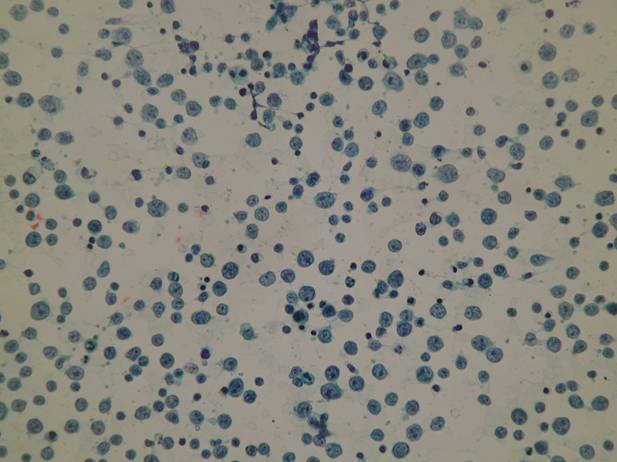
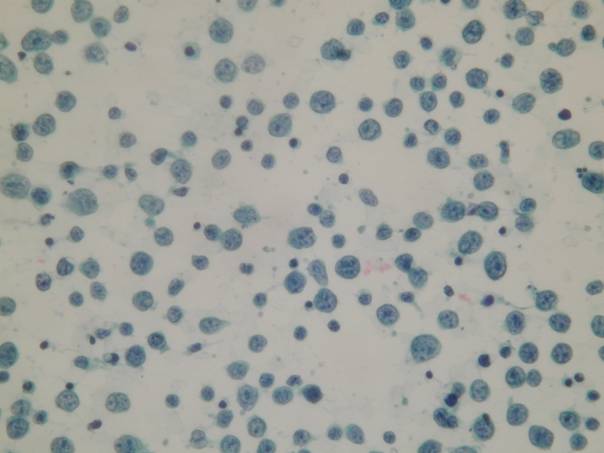
- high cellularity
- isolated lymphoid cells
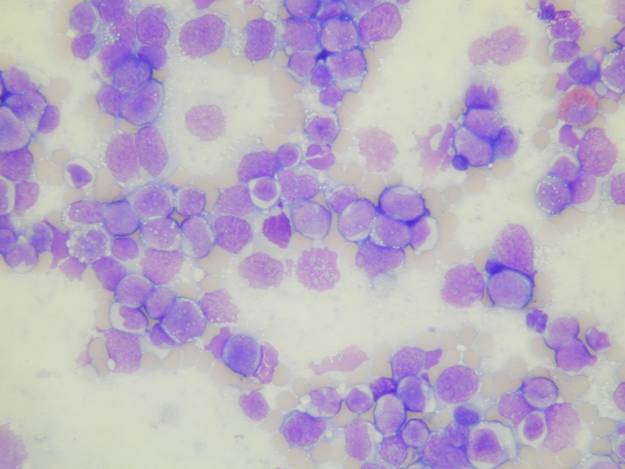
MZL type is predominantly composed of small lymphoid cells (centrocytes, plasma cells, monocytoid B cells) with interspersed large lymphoid cells. The characteristic lymphoepithelial lesions are difficult to see on smears. DLBL type is composed of large lymphoid cells (centroblasts, immunoblasts, Burkitt-like cells).
Differential diagnosis
- Hashimoto`s thyroiditis
The main differential diagnosis is Hashimoto`s thyroiditis. When large, highly atypical lymphoid cells are present, the differential diagnosis is not difficult. The small cell lymphomas are hard or impossible to distinguish from Hashimoto`s thyroiditis and immunophenotyping, carried out by flow cytometry or immunocytochemistry, is useful when lymphoma is suspected.
A pure lymphoid population devoid of epithelial cells. A homogeneous population made of large atypical lymphocytes (Pap). The dominant population is made of large, atypical lymphocytes (MGG).