Non-gynaecological Cytology
Thyroid cytology
Multinodular goitre
It is a nodular enlargement of the gland, due to derangements in hormone production, which is often asymmetric and sometimes extreme. Follicular cells undergo hyperplasia, leading to the formation of several nodules. The nodules, which are usually not encapsulated, may considerably vary in their microscopic appearance: some of them are composed of very large macrofollicles filled with colloid, others are more cellular with very little colloid. The growth of such nodules leads to hemorrhage, scarring, microcystic formation and dystrophic calcification.
Cytologic diagnostic features
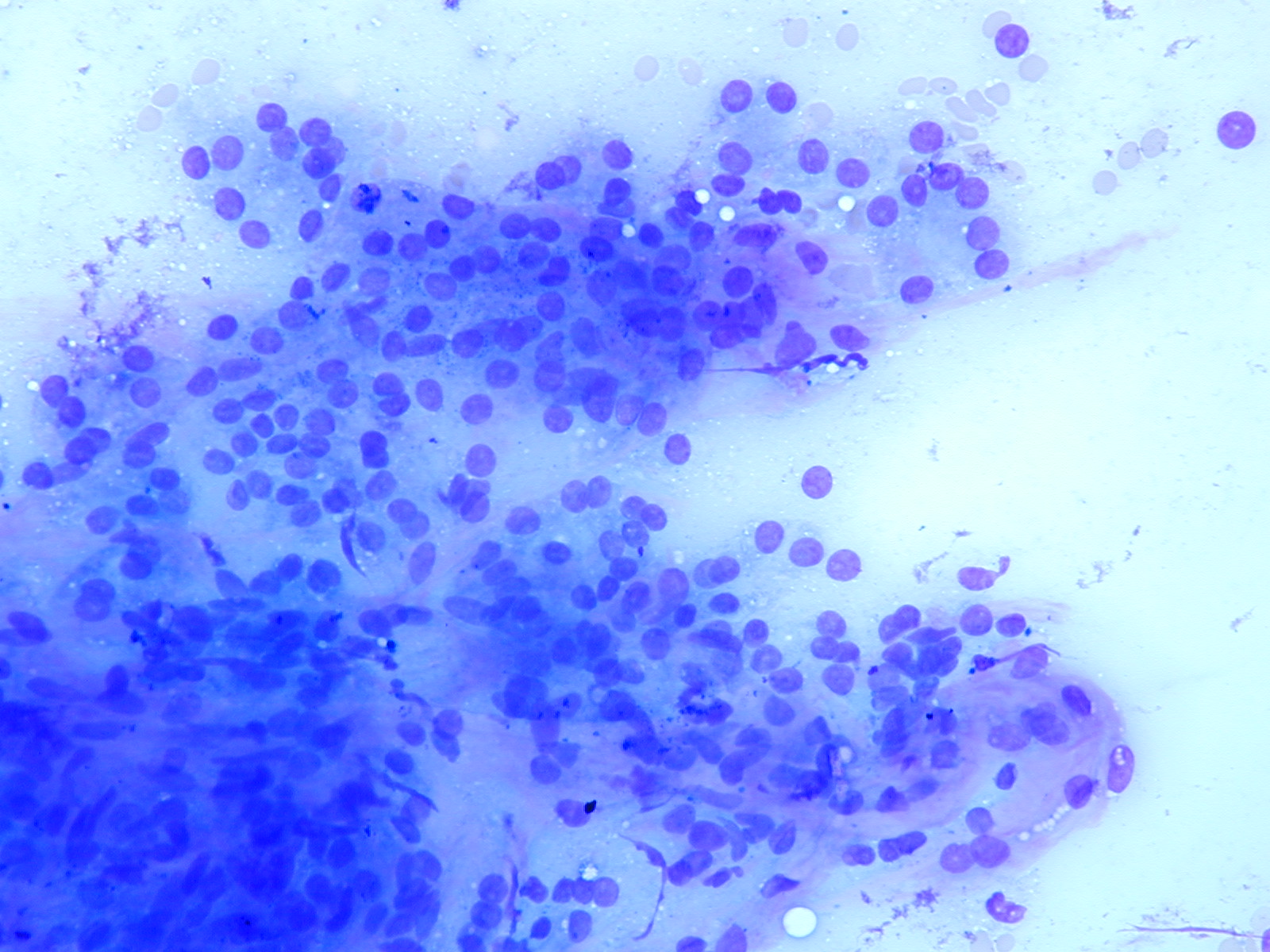
- bland thyrocytes in follicles or flat sheets
- abundant fluid colloid
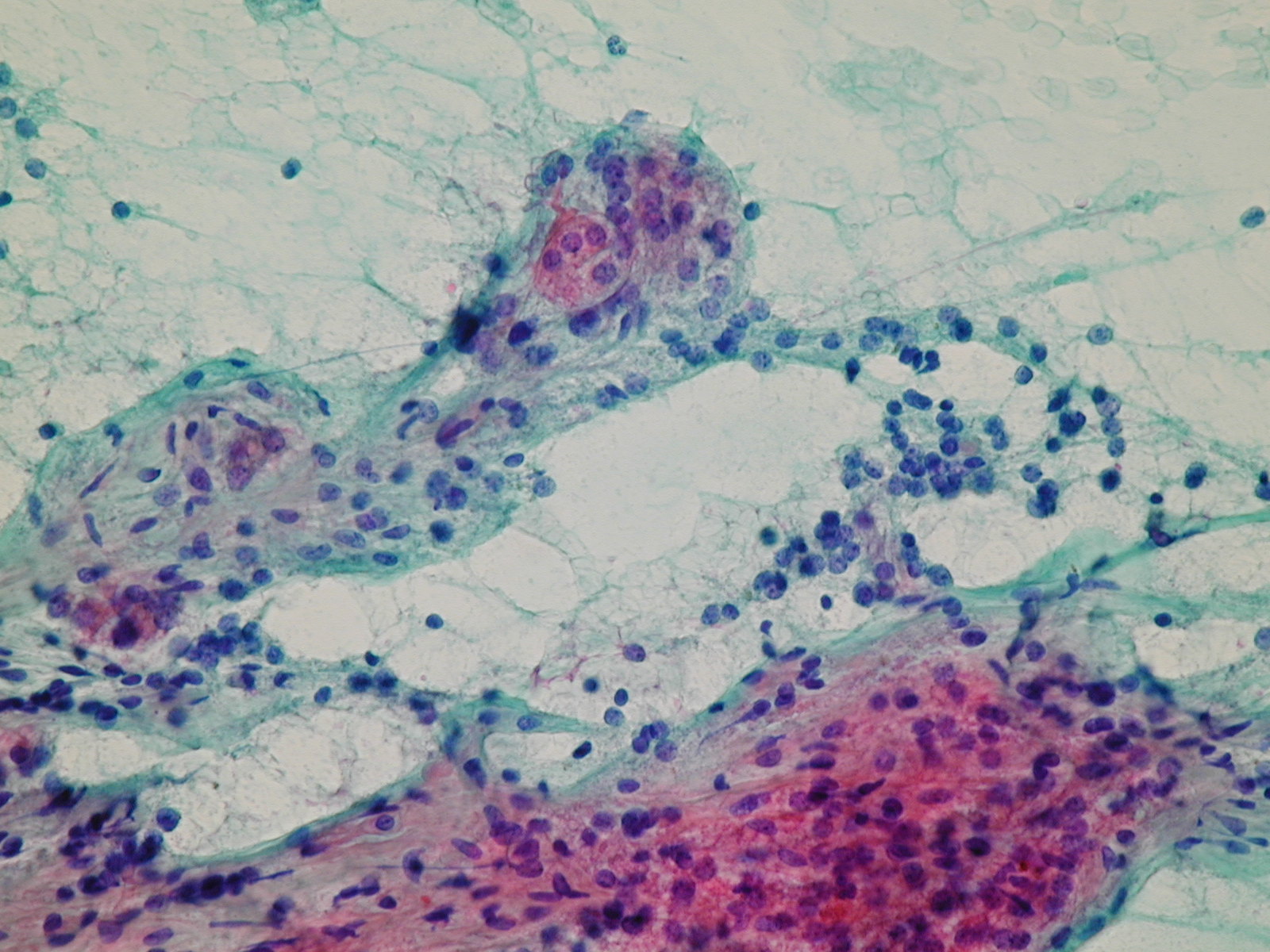
- foamy macrophages
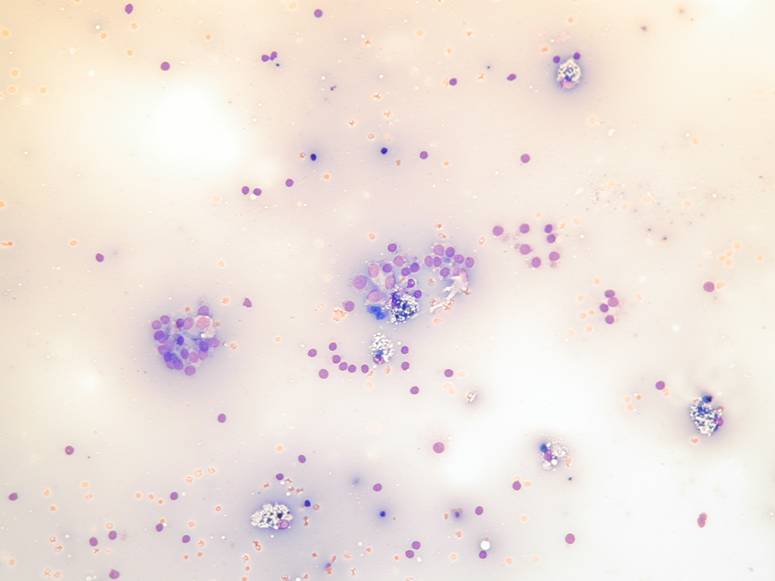
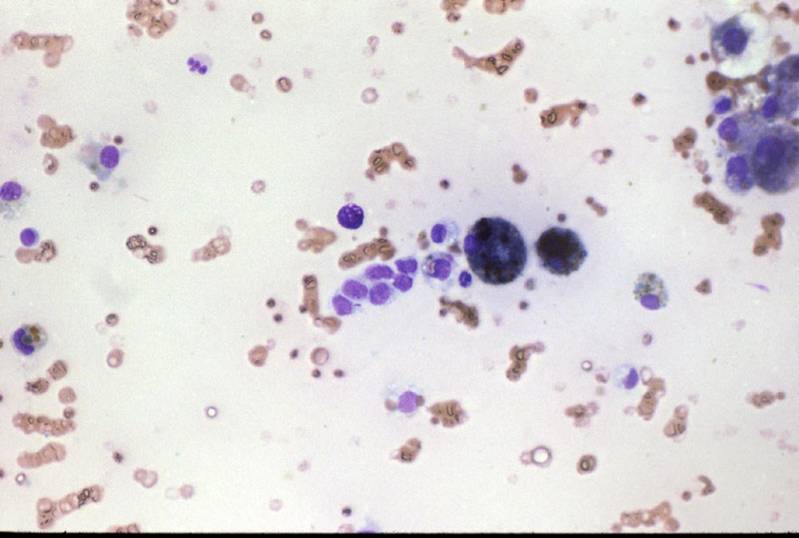
Fluid colloid with scattered follicles and histiocytes. Pigmented macrophages. Fluid colloid, bland epithelial cells and histiocytes.
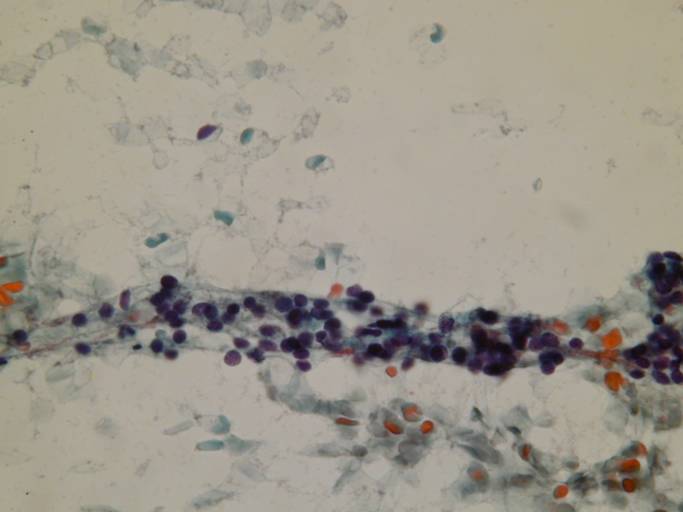
Pigmented and vacuolated macrophages, bland follicular cells. A streak of bland follicular cells.
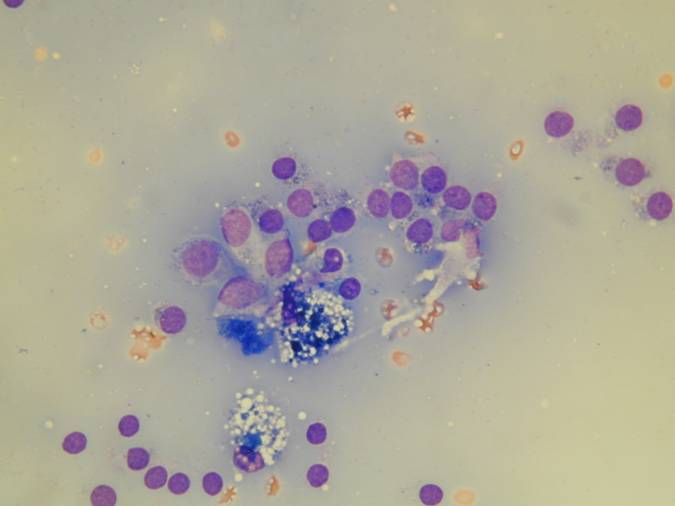
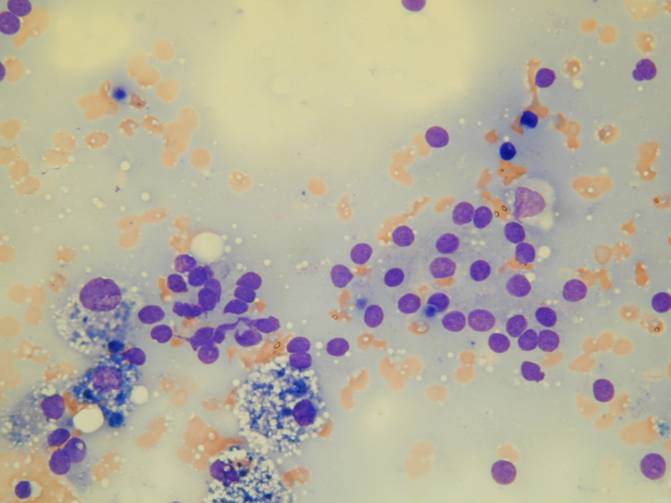
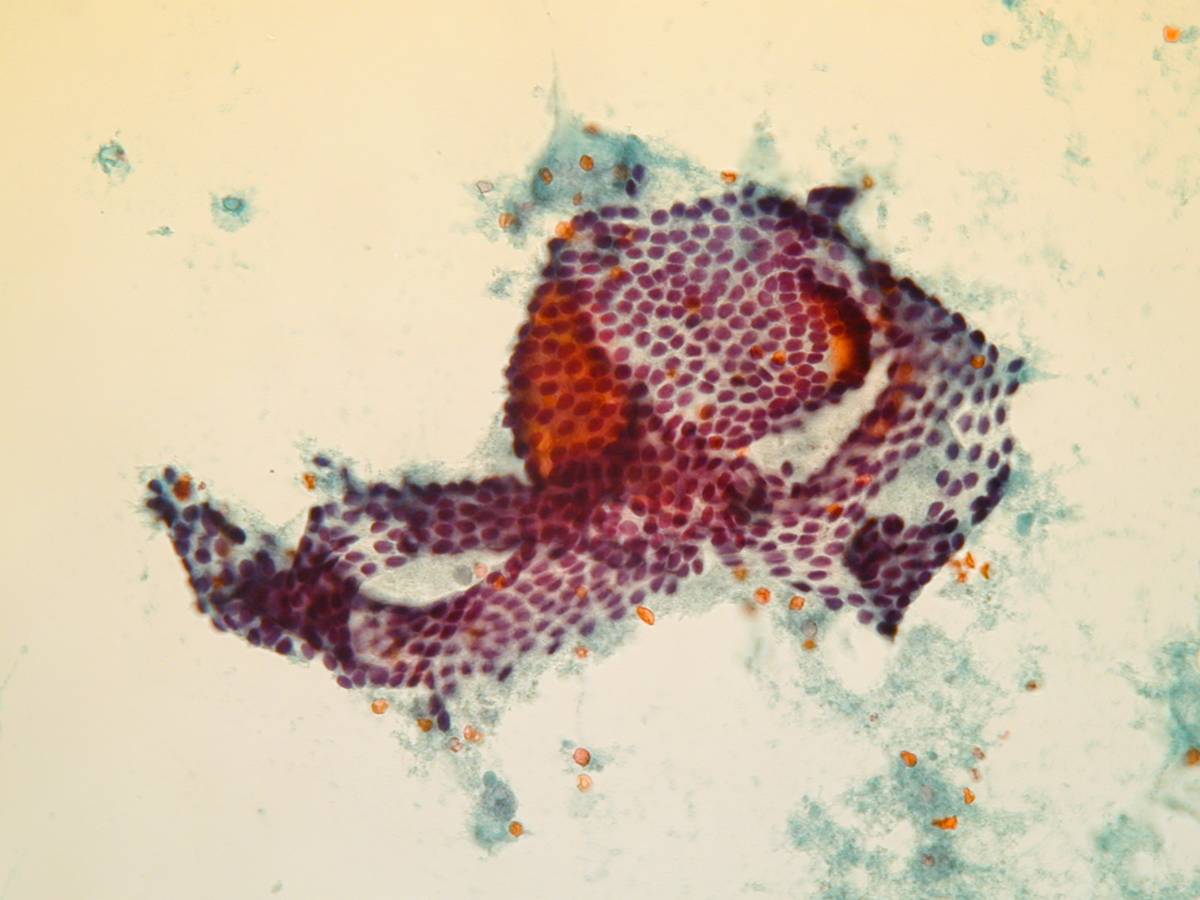
A folded sheet of bland epithelial cells. Bland follicular cells.
3D follicles. Bare nuclei.