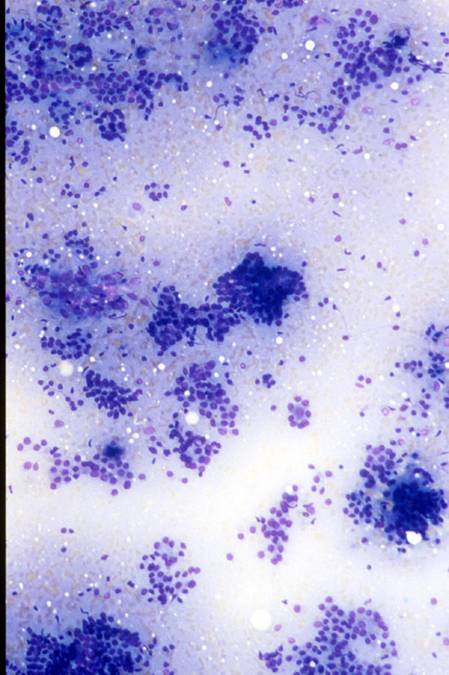
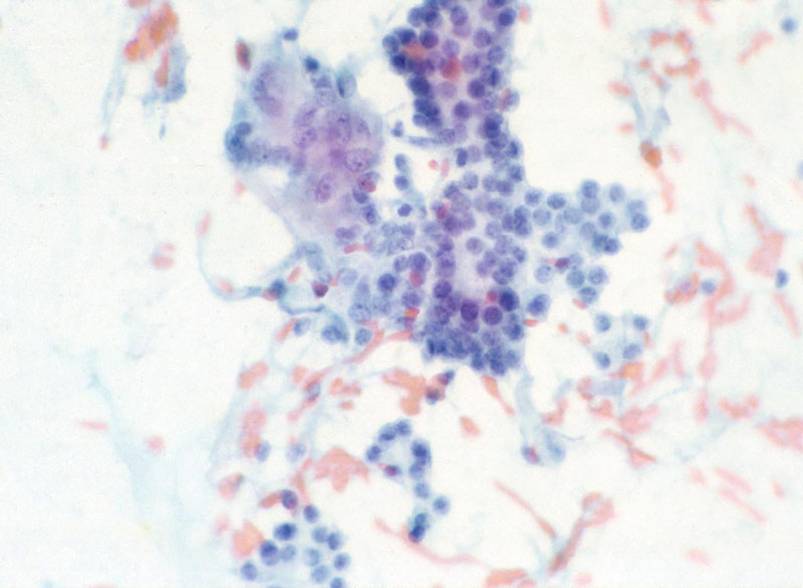
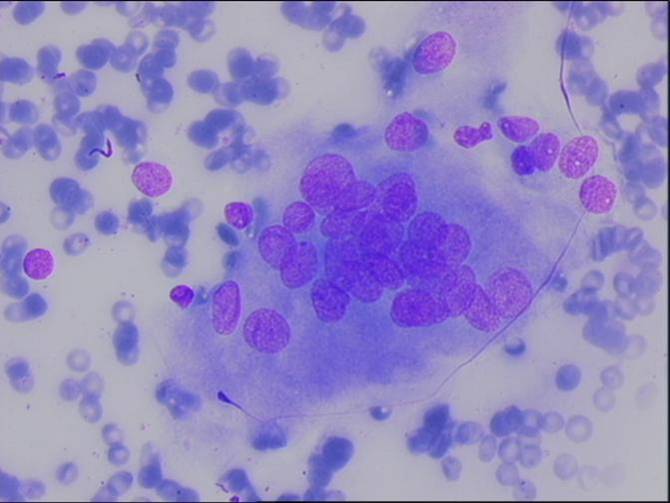
Subacute granulomatous (De Quervain`s) thyroiditis
It is a rare self-limited disease, usually lasting several months, characterized by a painful enlargement of the gland. It is a granulomatous inflammatory condition which leads finally to fibrosis of the gland.
Cytologic diagnostic features
- granulomas
- giant cells
- lymphocytes and neutrophils
The cytologic specimens contain nodular aggregate of hystiocytes, lymphocytes and neutrophils. Epithelioid cells and multinucleated giant cells of the granulomas are usually present, but are not specific of this condition. The follicular cells show degenerative features such as paravacuolar granules and sometimes Hürtle cells changes (eosinophilic granular cytoplasm and enlarged nuclei). Because of the fibrosis, aspirates may be hypocellular.
Differential diagnosis
- Hashimoto`s thyroiditis
The differential diagnosis includes inflammatory conditions such as Hashimoto`s thyroiditis, which can be clinically differentiated from subacute thyroiditis, and neoplasms (such as anaplastic carcinoma). The abundant granular or foamy cytoplasm and the chromatin pattern helps to identify the cells as benign hystiocytes.
A cellular aspirate from a subacute thyroiditis. A medium power view of an epithelioid granuloma. A multinucleated giant cell.