Citologia Cervicale
Modificazioni infiammatorie reazioni specifiche a infezioni, modificazioni iatrogene e aspetti riparativi.
| Cause and effect of injury to cervix |
| Non specific inflammatory changes |
| Specific infections |
| chronic cervicitis and folicular cervicitis |
| Regeneration and repair |
| Clinical notes |
Rigenerazione e riparazione
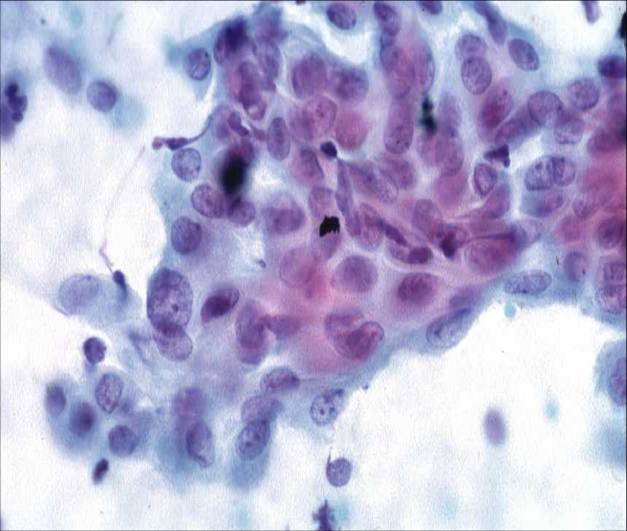
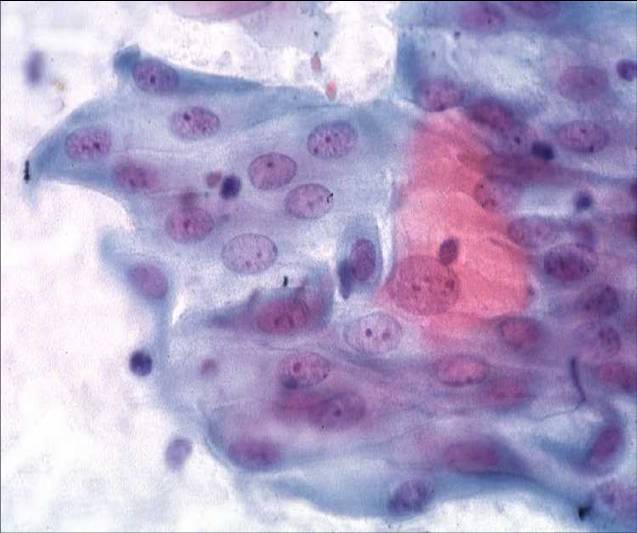
- La guarigione dell'epitelio eroso o ulcerato viene prodotta dalla proliferazione delle cellule dello strato basale dell'adiacente epitelio e dalla duplicazione delle cellule di riserva presenti nelle cripte delle ghiandole limitrofe. Inizialmente le aree diesepitelizzate sono rivestite da cellule metaplastiche immature che successivamente si trasformeranno in cellule squamose mature o cellule epiteliali colonnari
- Le alterazioni degenerative associate all' 'infiammazione e le modificazioni rigenerative sono spesso viste contemporaneamente all' interno dello stessi striscio.
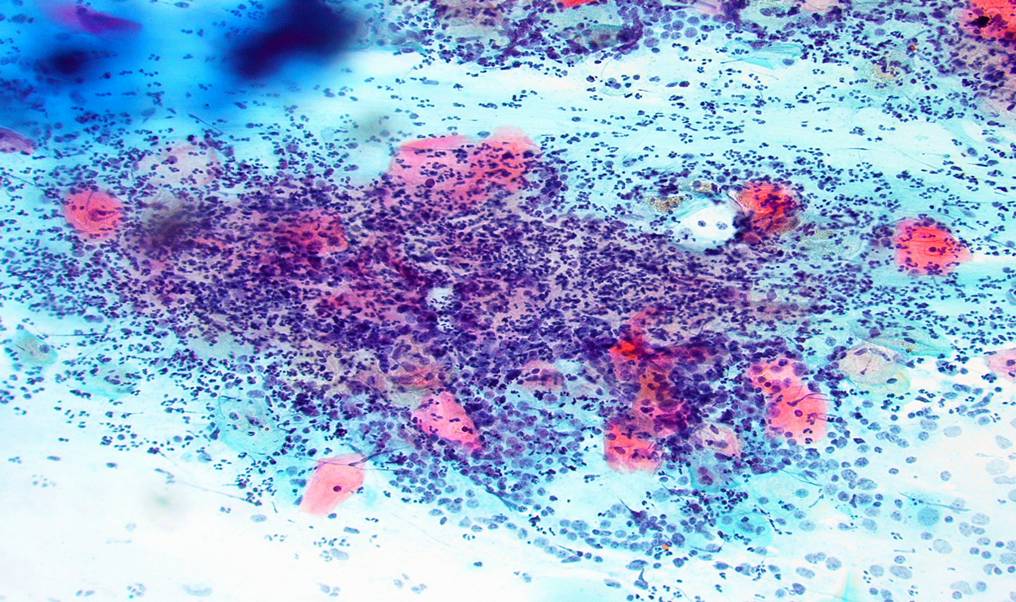
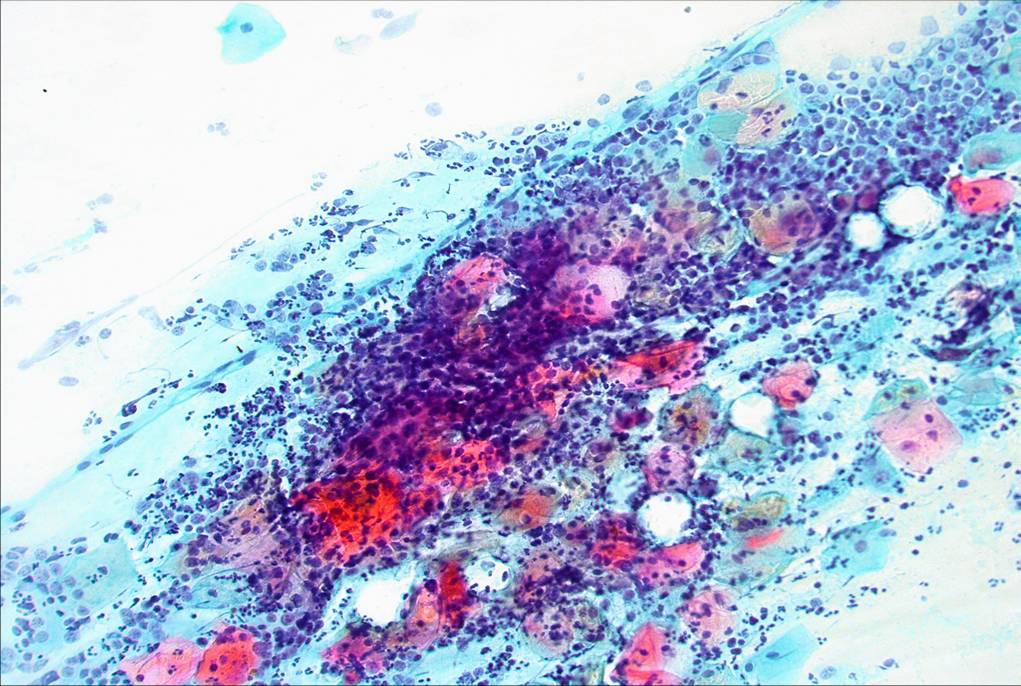
Cerviciti croniche
Quando il danno persiste una discreta quantità di linfociti e plasma cellule migra verso l'area infiammata, inoltre possono ritrovarsi abbondanti polimorfonucleati. Nelle cerviciti di lunga durata, come quelle associata all'inserzioni di anelli vaginali per evitare il prolasso nelle donne in post menopausa, l'epitelio può mostrare alterazioni reattive come paracheratosi e ipercheratosi. Queste modificazioni possono poi essere ritrovate negli strisci