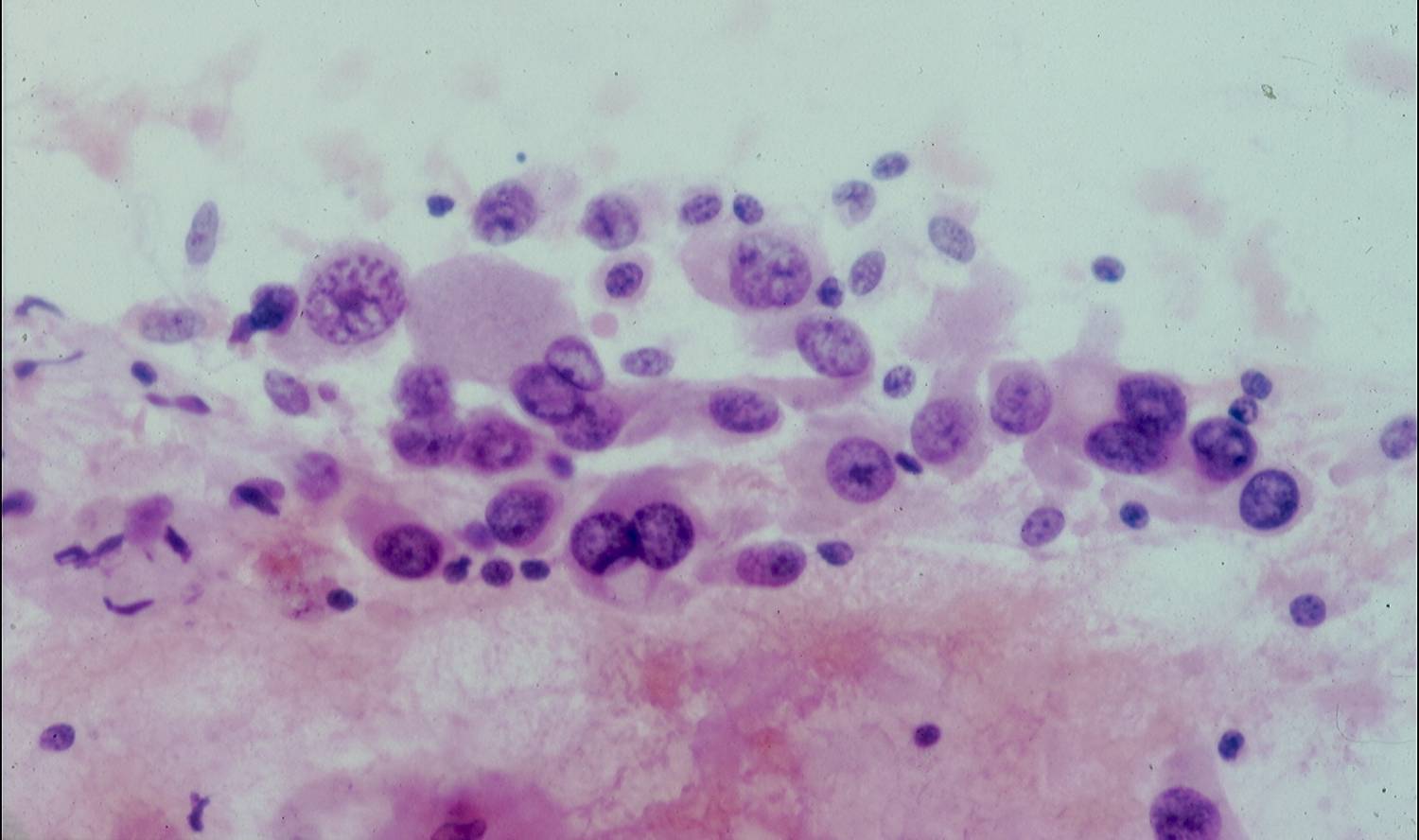
Adenocarcinoma
It is a common type of lung cancer and its incidence is increasing, particularly in women. Adenocarcinoma is the one cell type of primary lung tumor that occurs more often in non-smokers and in smokers who have quit. Most adenocarcinomas arise in the periphery of the lung.
Bronchioloalveolar carcinoma is considered as a variant of adenocarcinoma.Histologic subtypes:
- acinar
- papillary
- bronchioloalveolar carcinoma
- non-mucinous
- mucinous
- mixed mucinous and non-mucinous or indeterminate cell type
- solid adenocarcinoma with mucin
- adenocarcinoma with mixed subtypes
Rare variants:
- well-differentiated fetal adenocarcinoma
- mucinous ('colloid') adenocarcinoma
- mucinous cystadenocarcinoma
- signet-ring adenocarcinoma
- clear cell adenocarcinoma
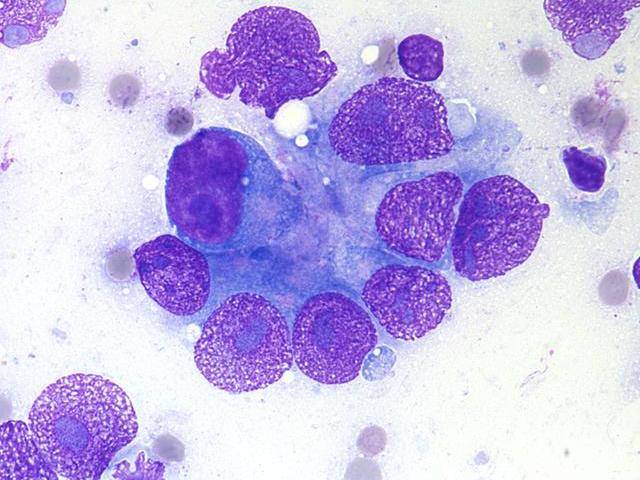
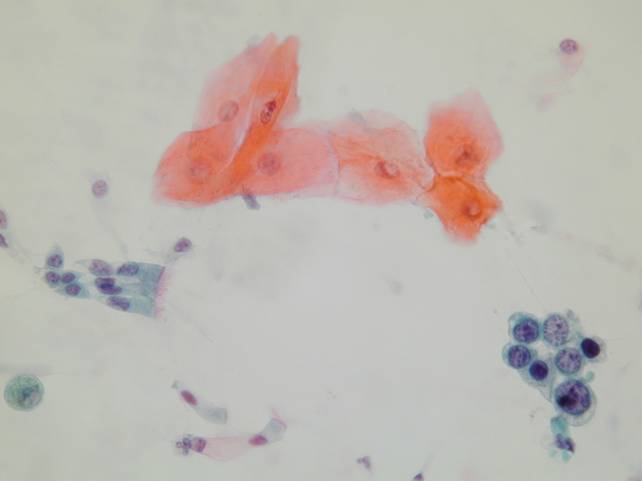
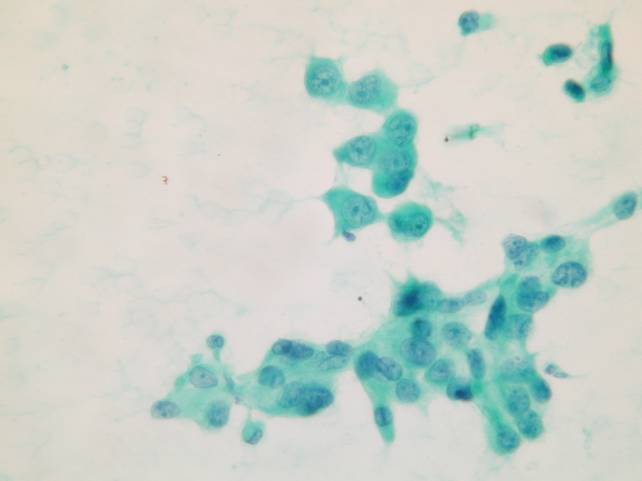
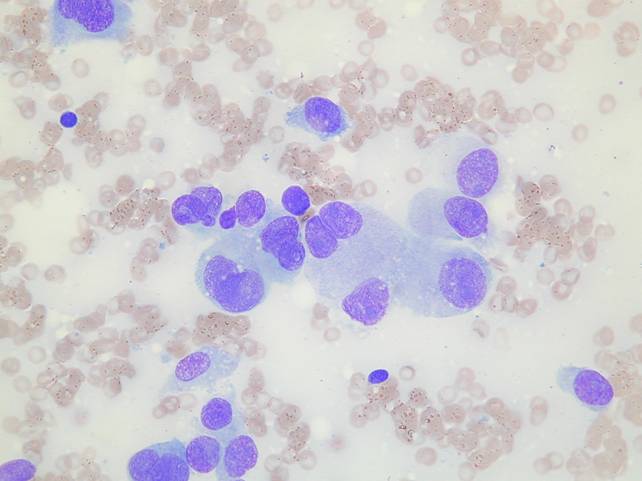
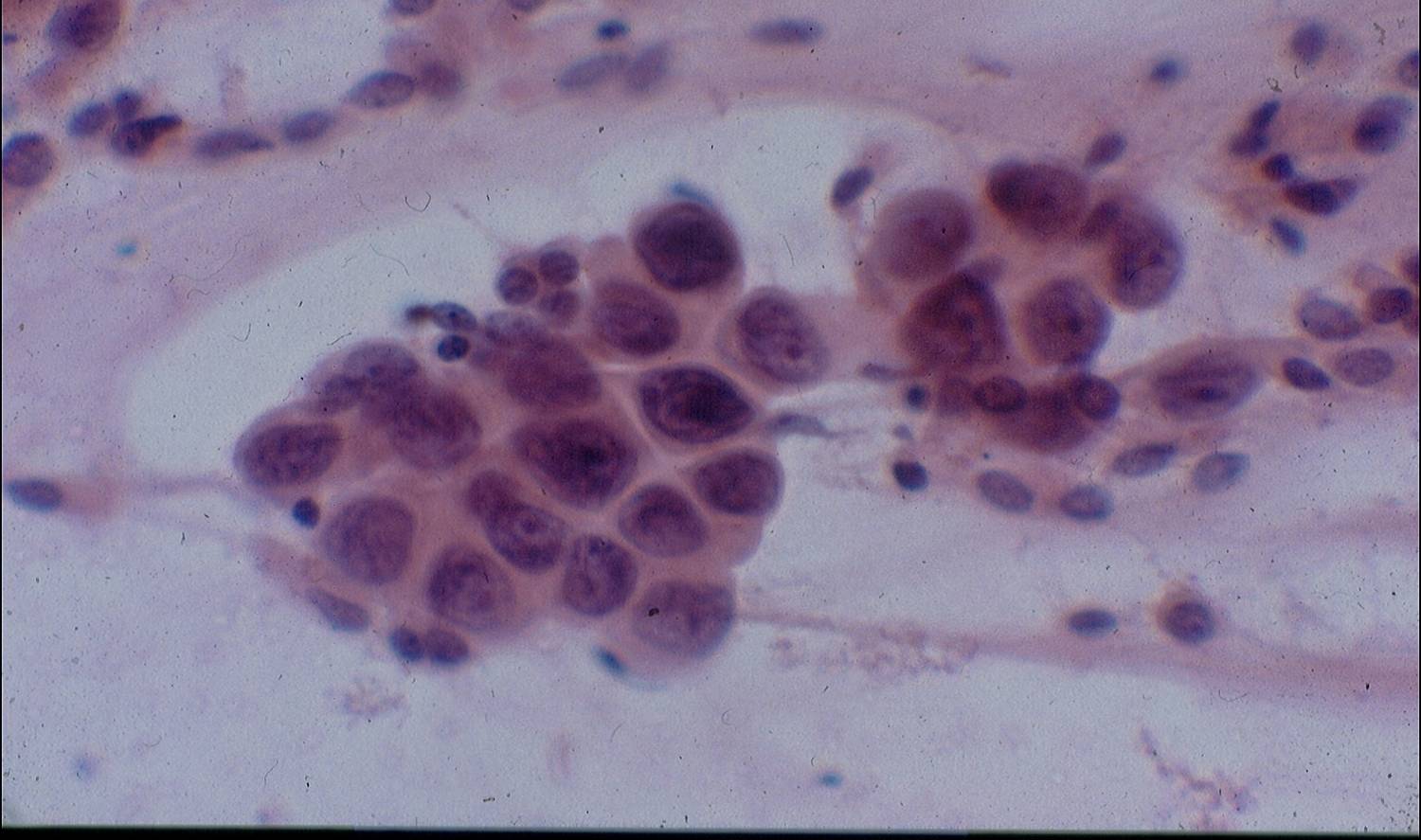
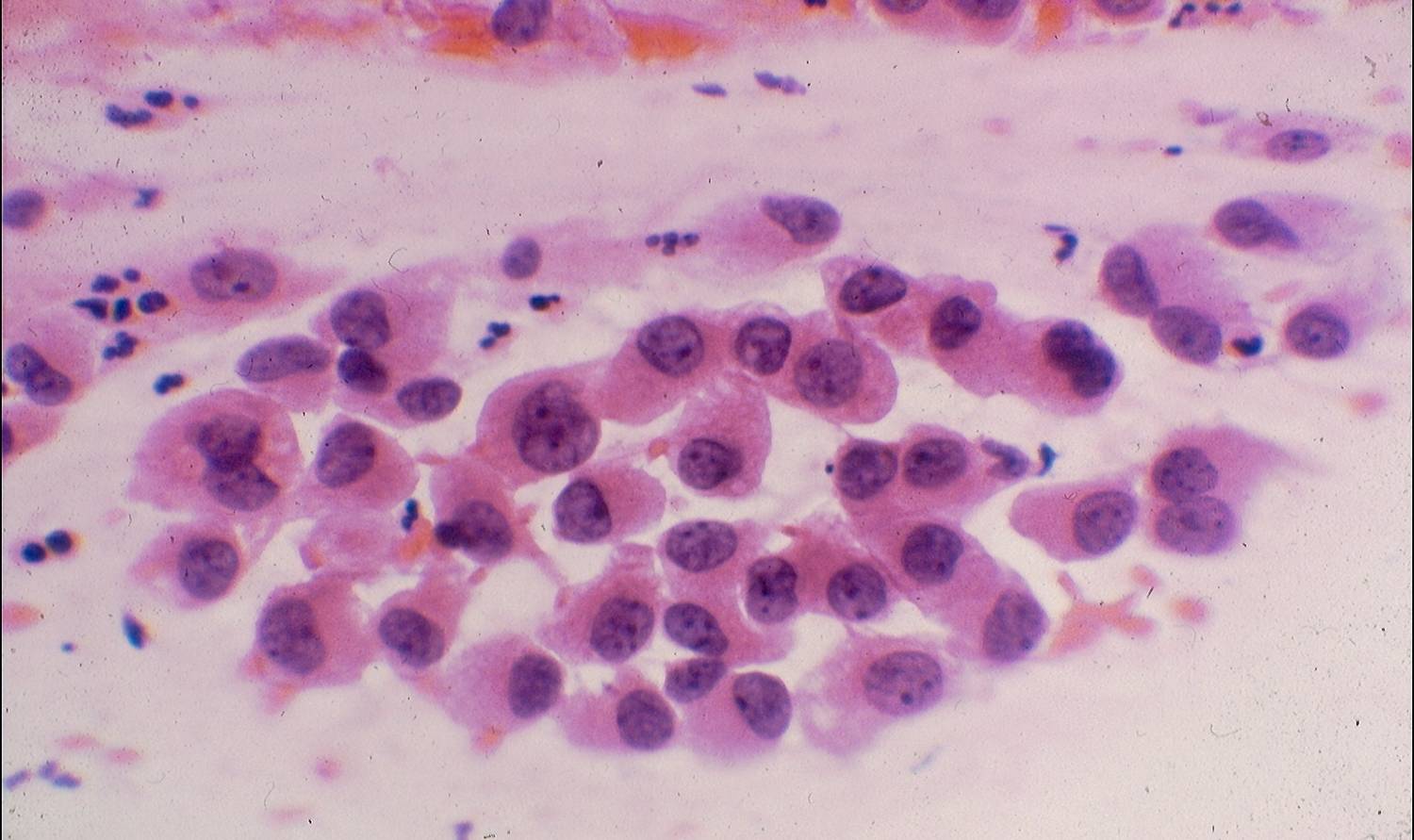
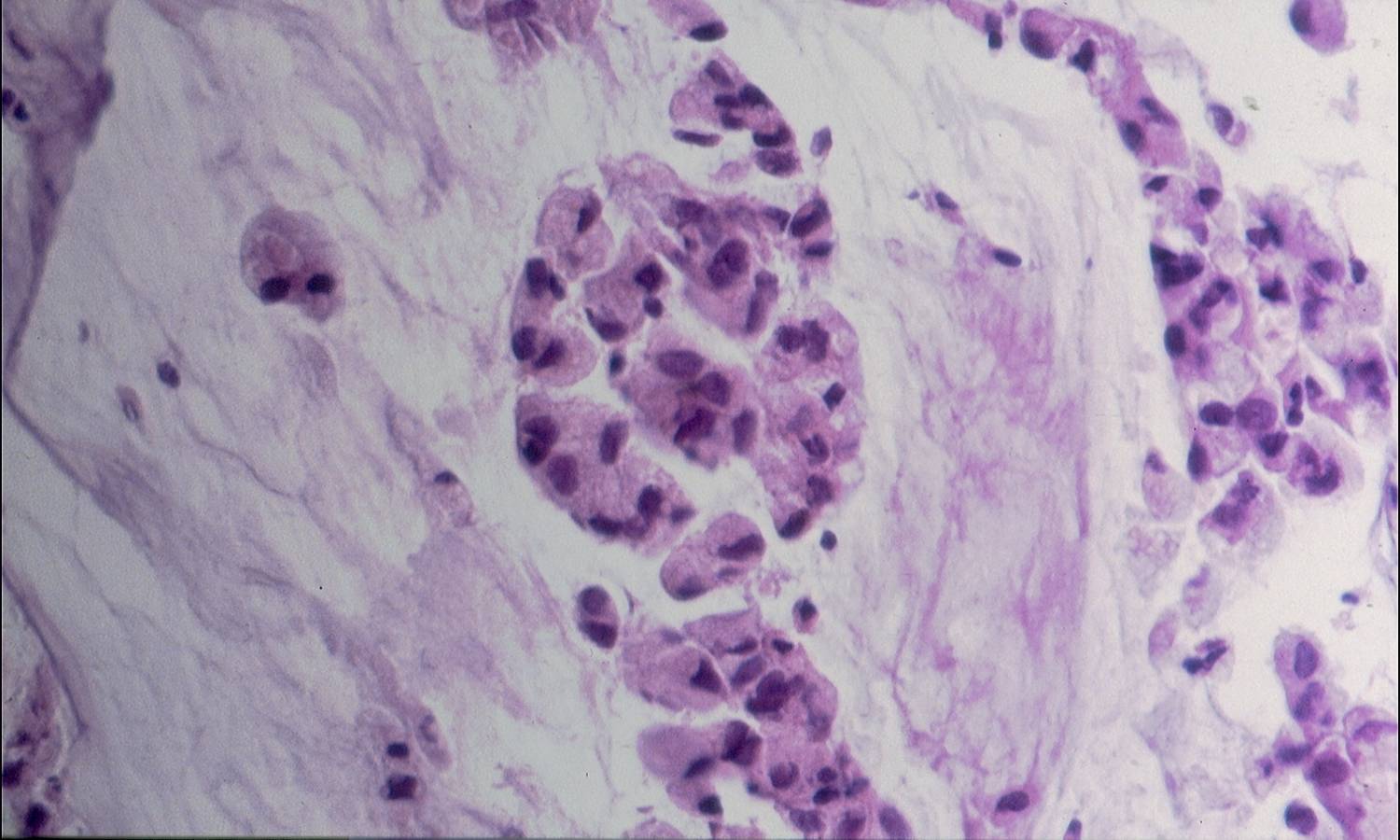
Cytologic diagnostic features (sputum and bronchial washing)
- Cell aggregates
- Large eccentric pleomorphic nuclei
- Prominent nucleoli
- Abundant pale vacuolated cytoplasm
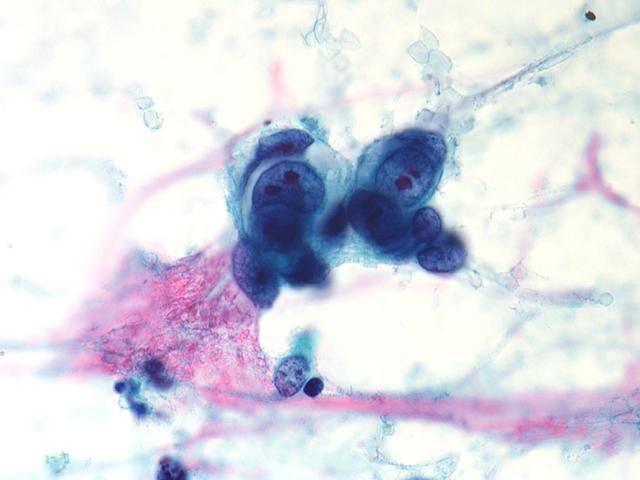
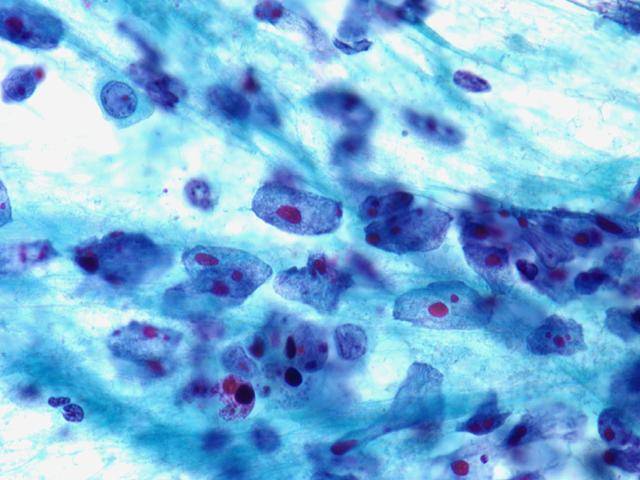
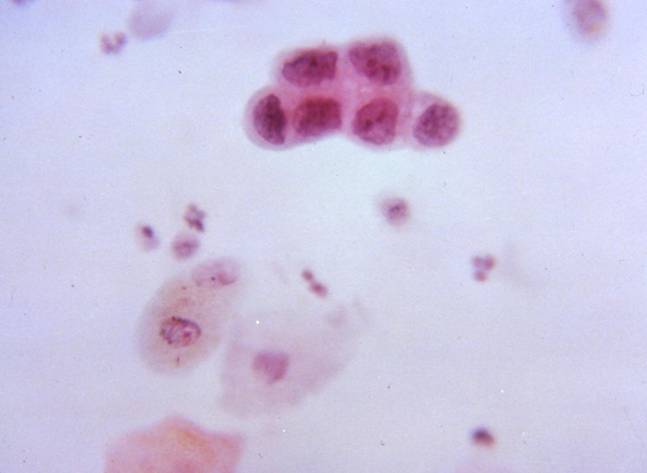
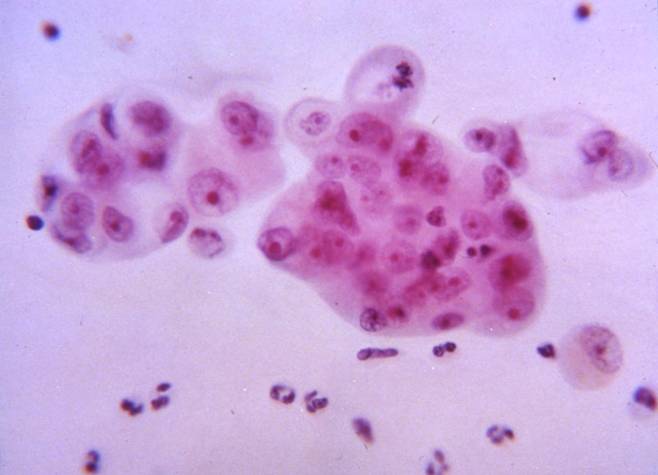
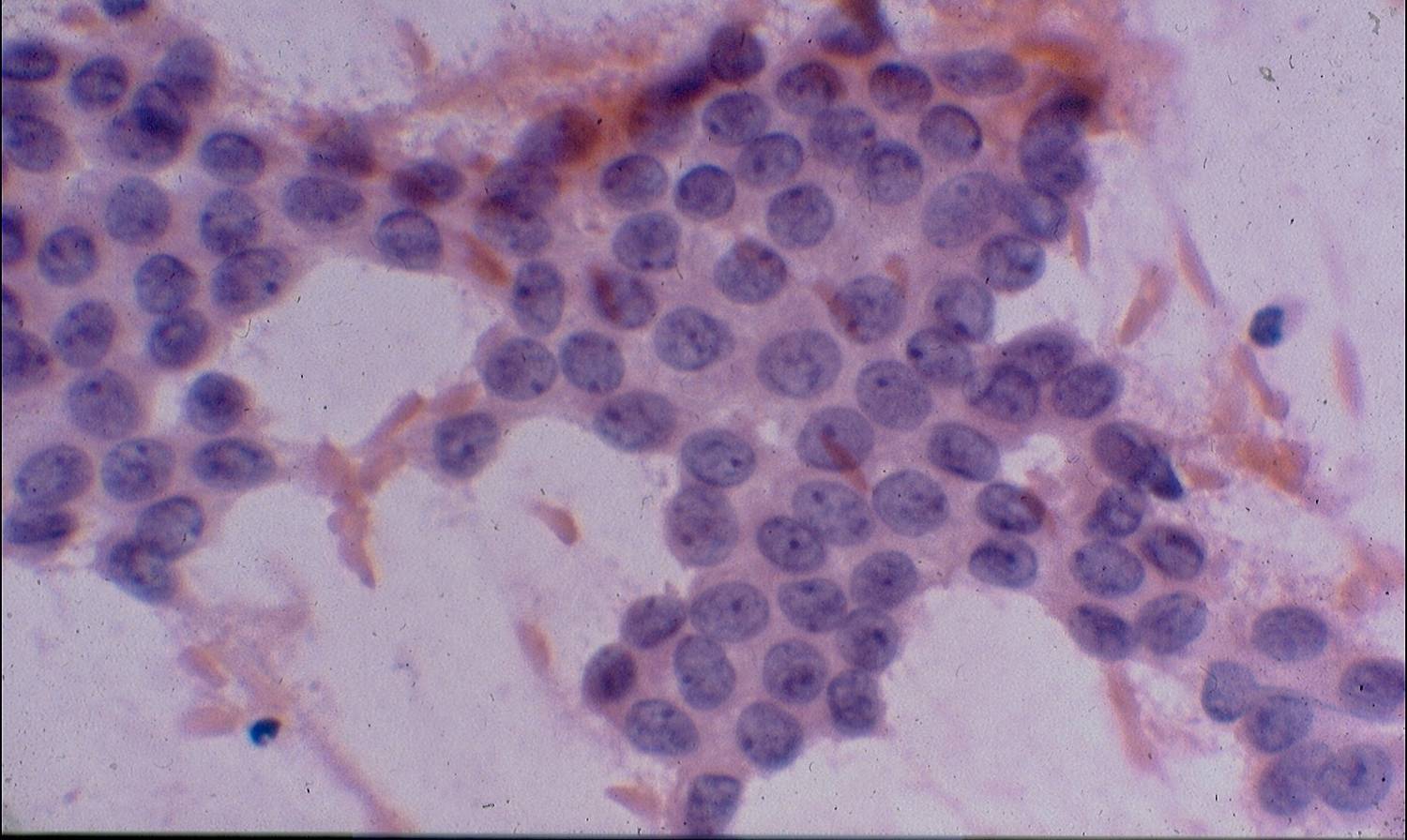
Cytologic diagnostic features (FNA and bronchial brushing)
- Sheets, rosettes and acinar grouing, columnar cells and mucin production
- Rounded nuclei
- Prominent nucleoli
- Abundant pale vacuolated cytoplasm
- Clean or mucinous background
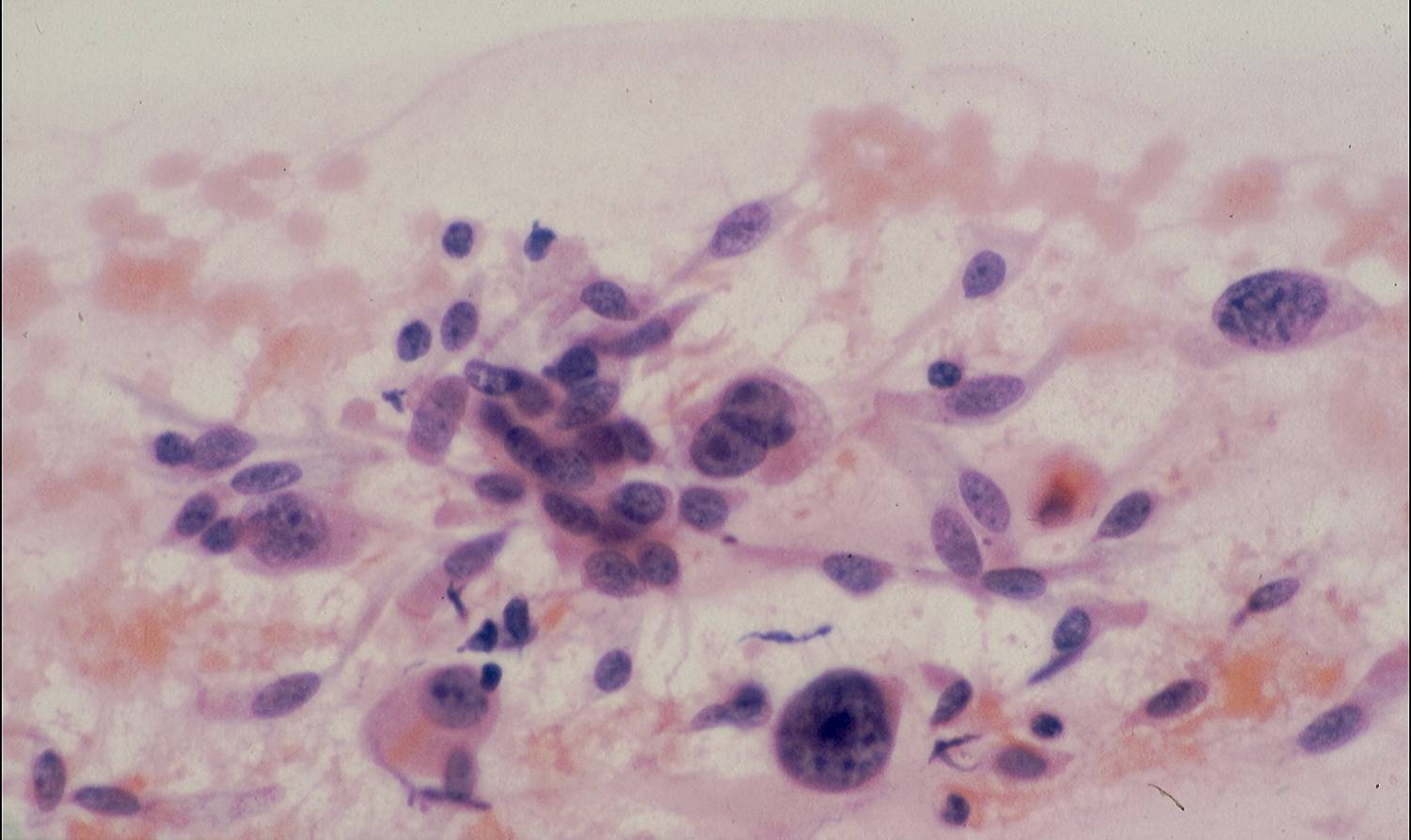
Differential diagnosis
- Metastatic adenocarcinoma
- Reparative/reactive bronchial epithelium
- Creola bodies
- Goblet cell hyperplasia
- Reactive pneumocytes
- Granulomatous inflammation
The cells of adenocarcinoma, except for poorly differentiated tumors, are more cohesive than those of squamous cell carcinoma. Poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma can be indistinguishable from large cell undifferentiated carcinoma with routine stains, but adenocarcinoma is positive for intracytoplasmic mucin.
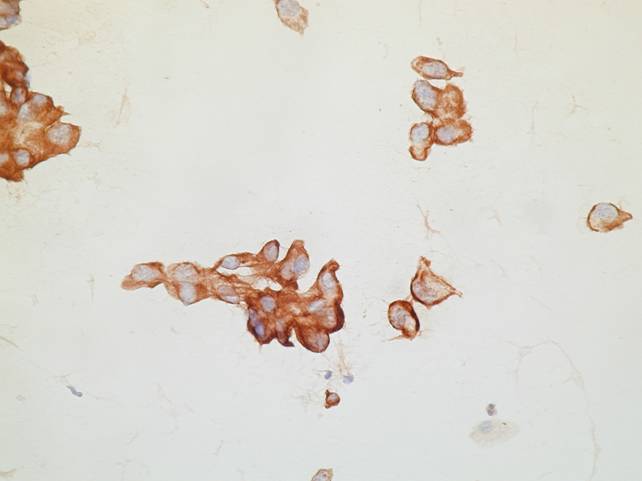
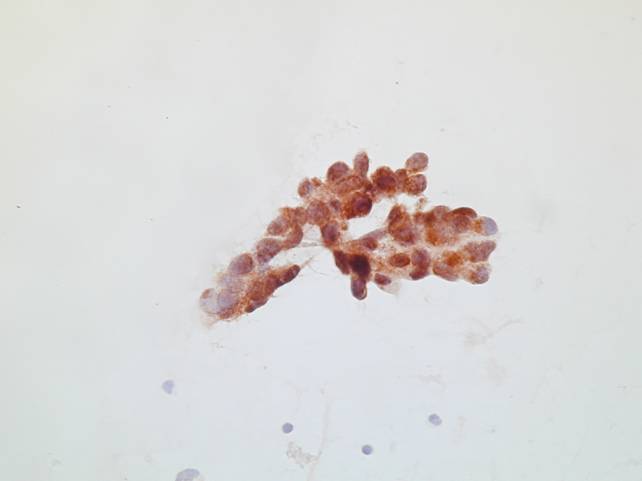
Immunocytochemistry
- Cytokeratin 7 +
- Cytokeratin 5 –
- Cytokeratin 20 –
- Neuroendocrine markers +-
- TTF-1 +
FNA FNA FNA