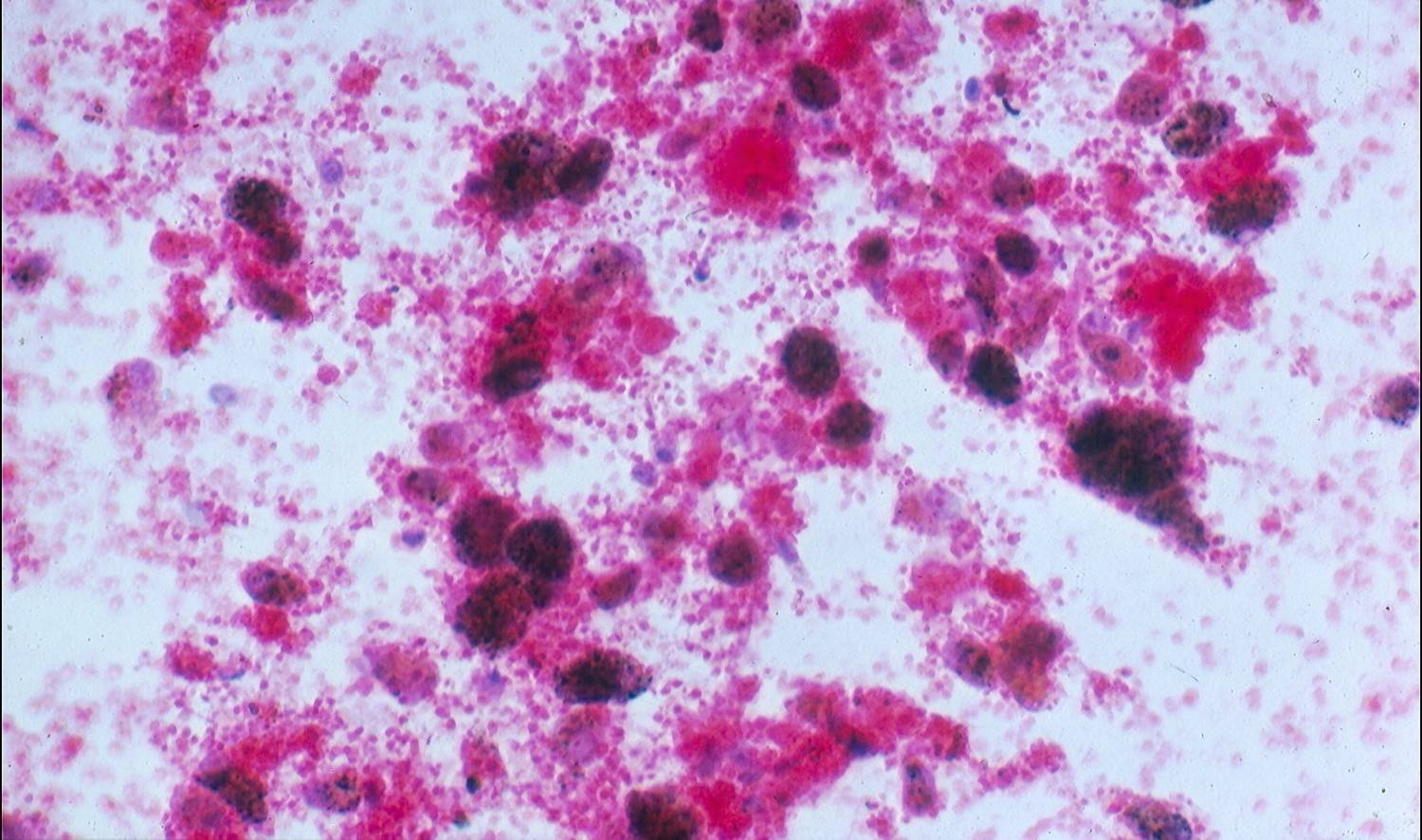
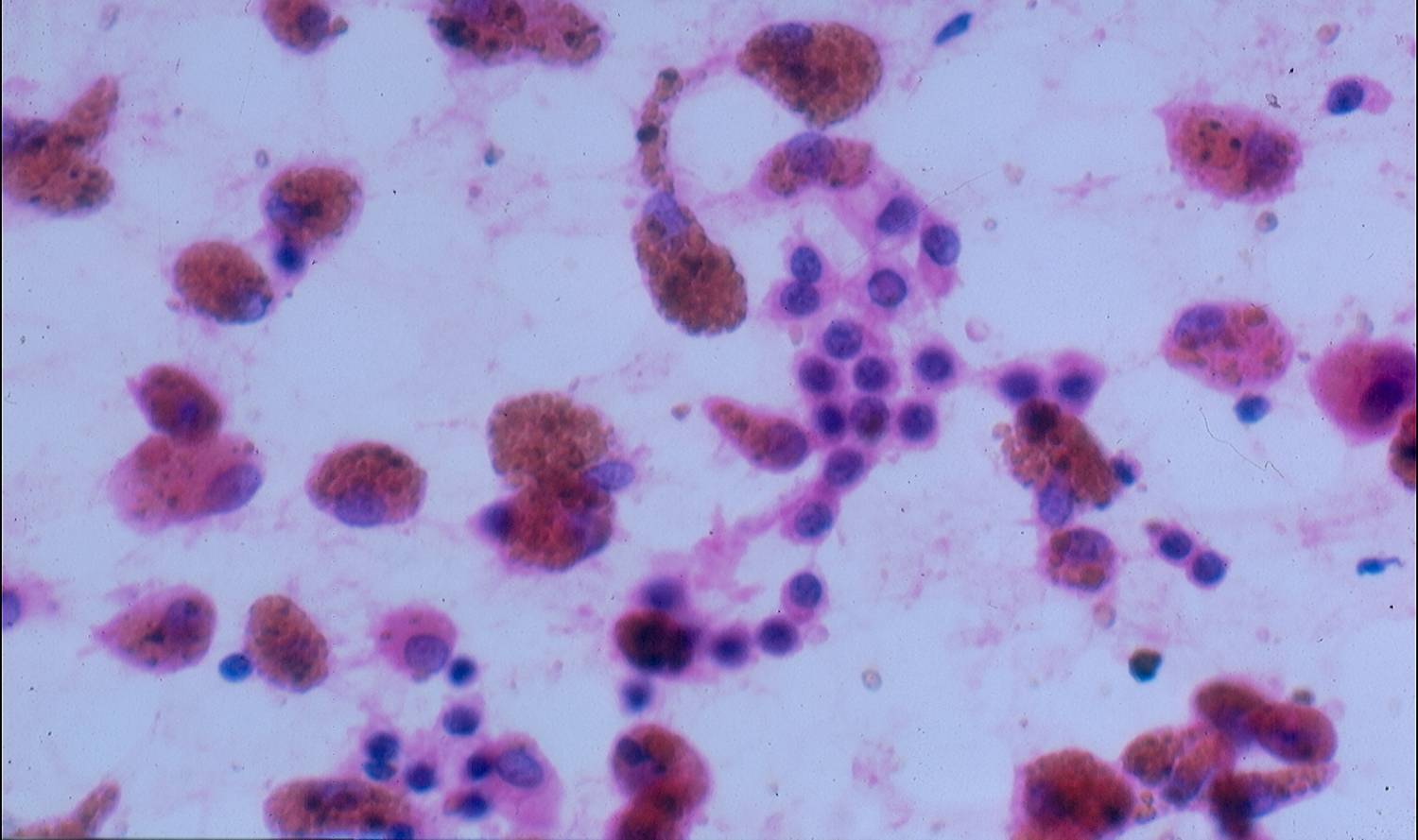
Inflammation
The cytologic features of common inflammatory processes, such as organizing pneumonia, bronchiolitis obliterans obstructing pneumonia and diffuse alveolar damage, are considerably overlapping. Inflammatory cells are observed, such as macrophages, neutrophils, eosinophils and lymphocytes. Reactive pneumocytes are especially common in organizing pneumonia and diffuse alveolar damage.
The lung is the most common site of sarcoidosis, which is characterized by non-caseating granulomas in many organs. The cause of the disease has not been identified.
Aggregates of epithelioid histiocytes, sometimes with Schaumann and asteroid bodies, are observed together with multinucleated giant cells and lymphocytes.Wegener`s granulomatosis is a necrotizing granulomatous vasculitis which may present as a pulmonary mass with or without involvement of other organs. Neutrophils, giant cells and epithelioid histiocytes are observed in a characteristic granular background debris consisting of necrotic collagen.
Pulmonary infarct
FNA negative - infarct