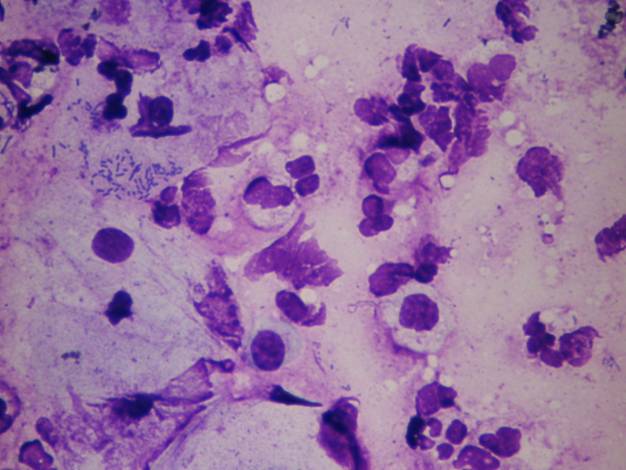
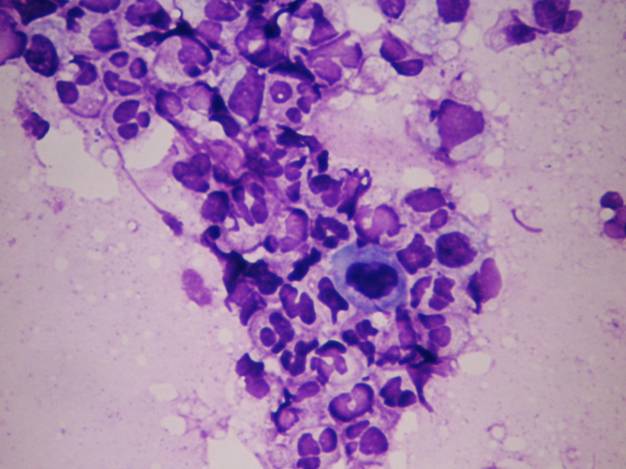
Exfoliative cytology of oral cavity
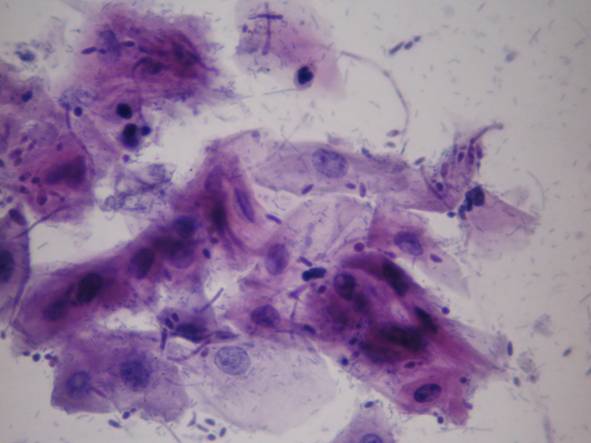
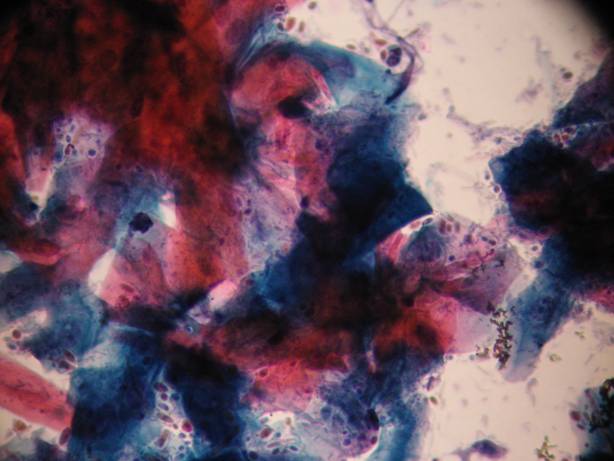
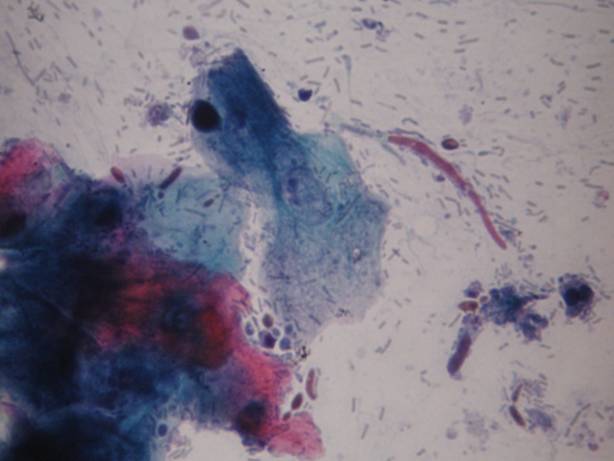
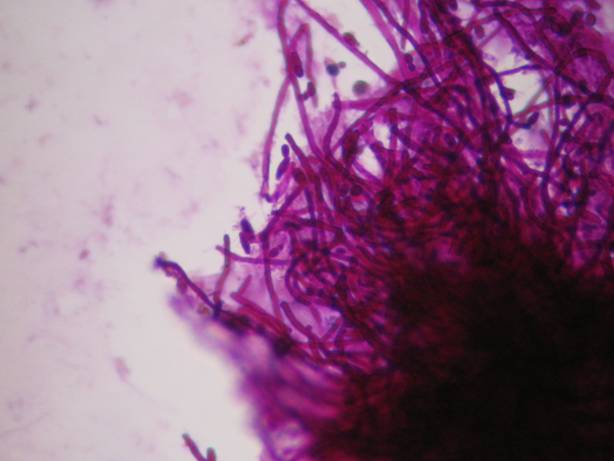
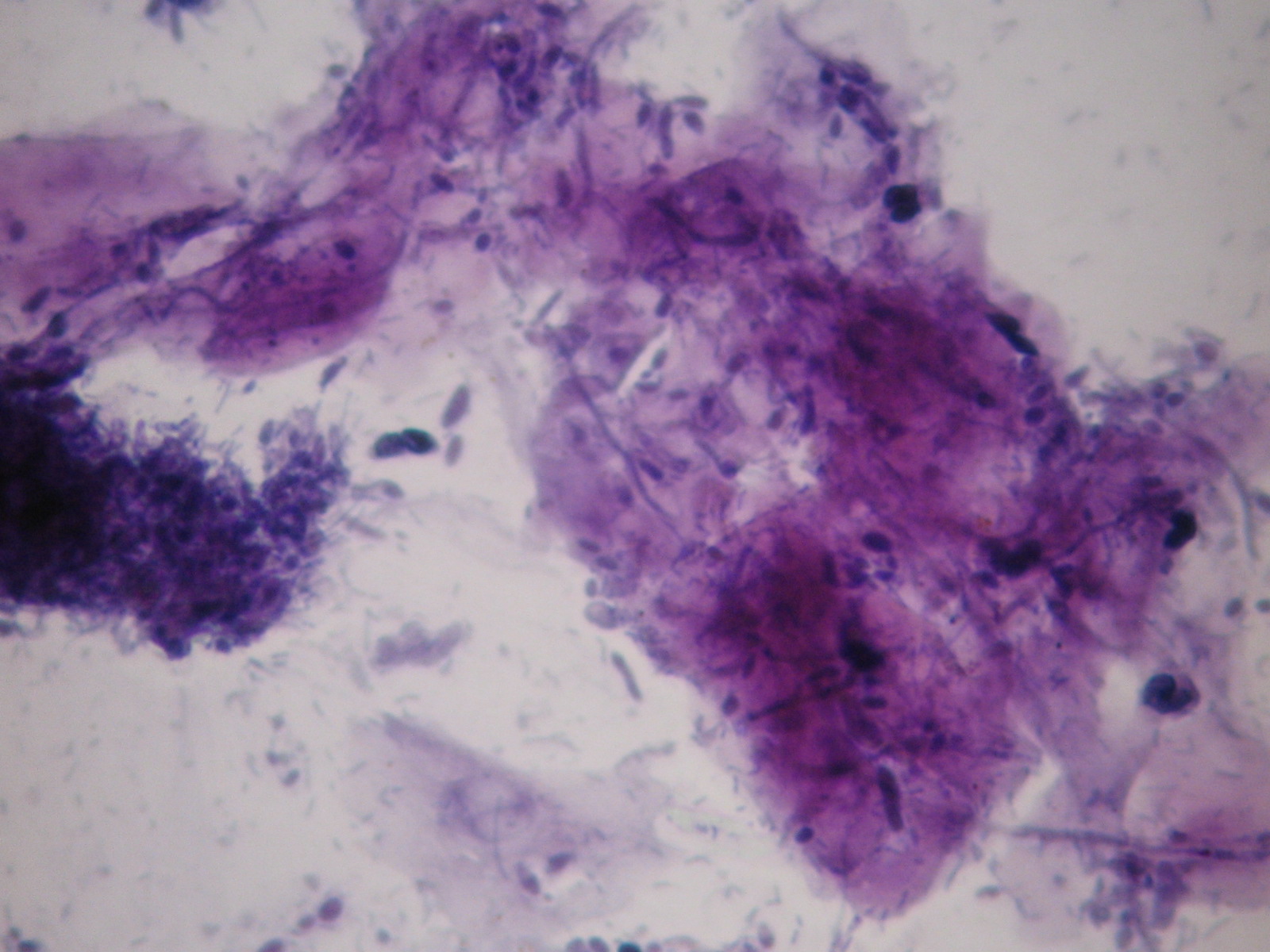
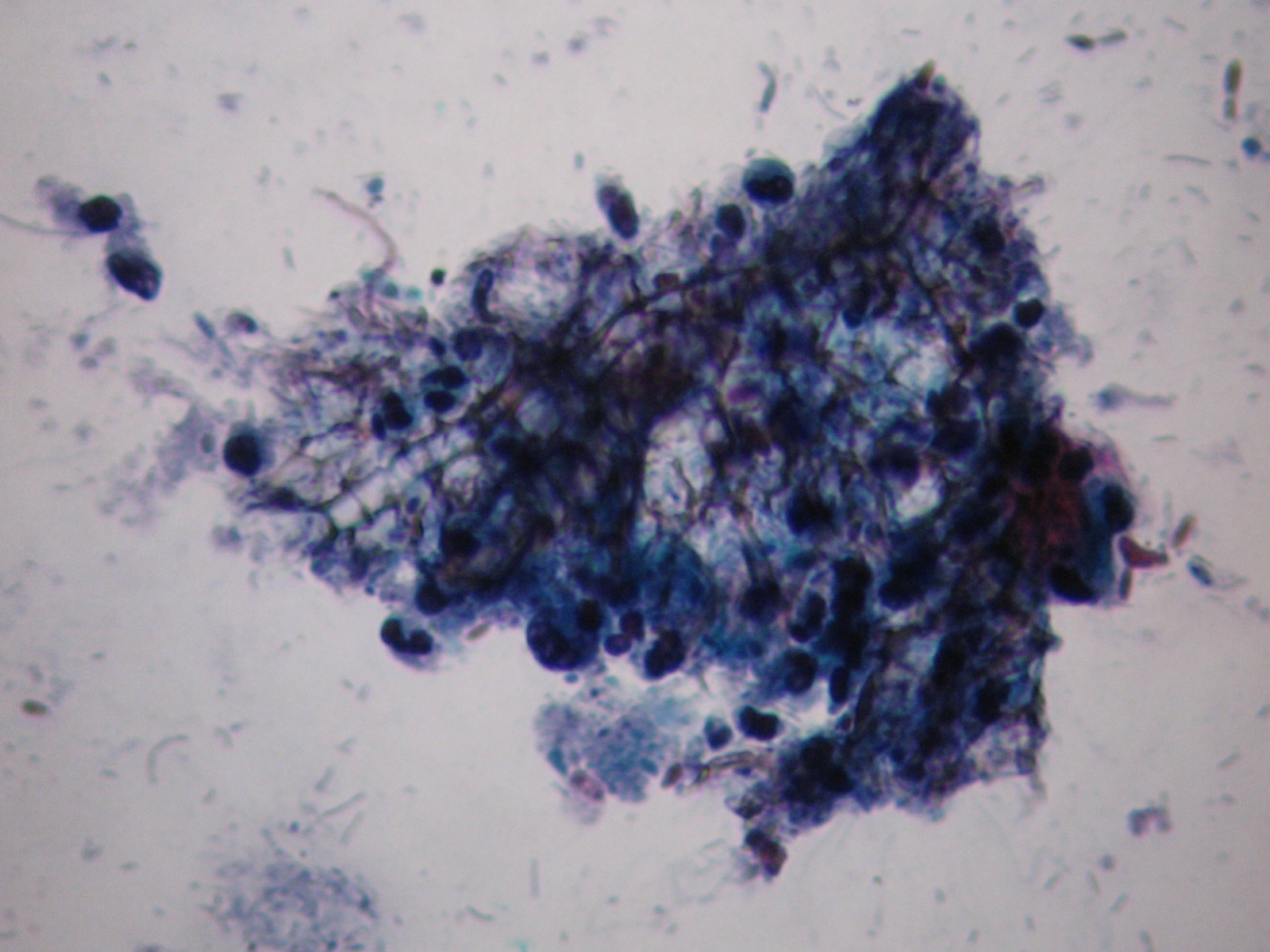
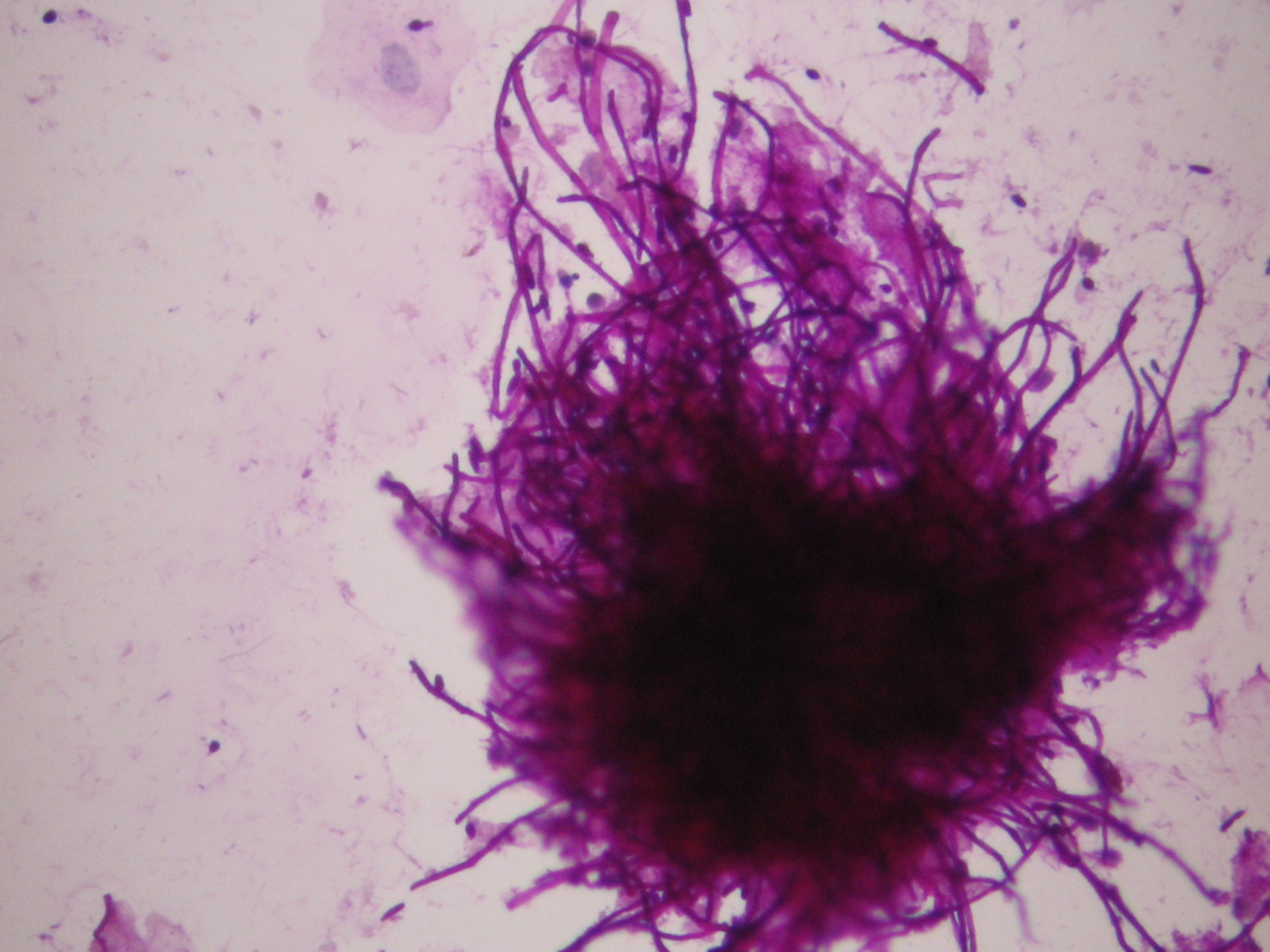
Infections without inflammation (AIDS): cells of the superficial squamous epithelium in a dirty background which contains many different types of infectious agents, such as bacteria, fungi, etc. The complete absence of inflammatory cells is diagnostic in these cases!
Squamous cell carcinoma of the oral mucosa shows very high incidence in Melanesia, France, Hungary, Western Europe. It can be sampled using cytobrush, or oral washing fluid can be prepared by using any kinds of LB techniques. The morphology of the cells is exactly the same as in the uterine cervical squamous cell carcinoma. Probably the best method for staining in this case is Papanicolaou stain.
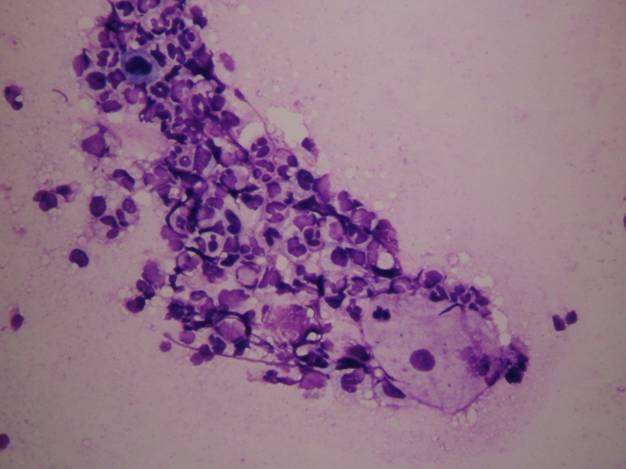
Pemphigus vulgaris and its variants show the presence of bullous lesions. The content of the vesicula or bulla can be smeared using cytobrush technique. One of the earliest cytology diagnoses was that of the recognition of the Tzanck cells: they are large, acantolithic cells with large pale nucleus and sometimes large nucleolus. The background shows features of acute inflammation.
Palpable lesions of the tongue are very rare. They can be aspirated. Squamous cell carcinoma is superficial, whereas non epithelial (usually benign) tumors are deep lesions.