Bronchioloalveolar carcinoma
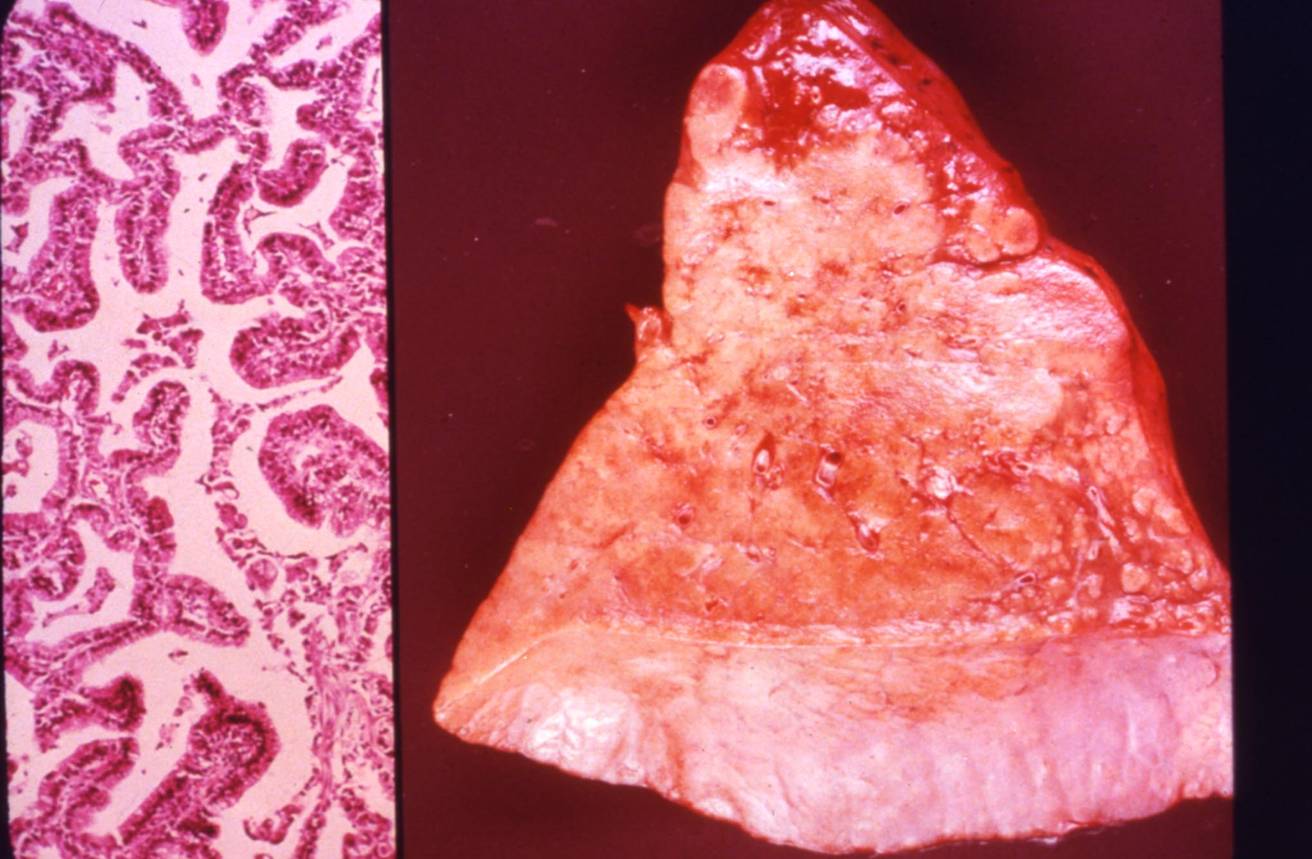
It is considered as a variant of pulmonary adenocarcinoma, accounting for about 5% of lung cancers. It is often multifocal, grossly appearing as a pneumonic consolidation. A characteristic feature is its growth along alveolar septa (lepidic growth pattern), without destroying the underlying alveolar architecture. Two subtypes are recognized: the cuboidal non-mucinous type and the mucinous type.
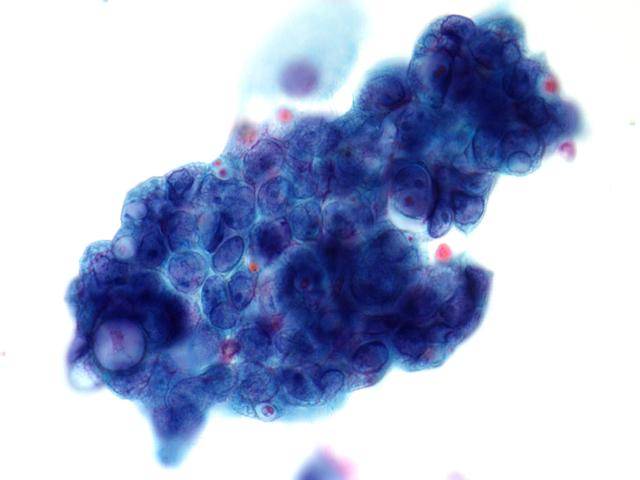
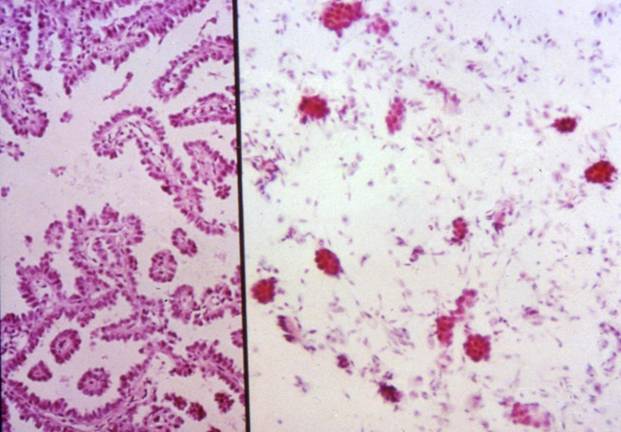
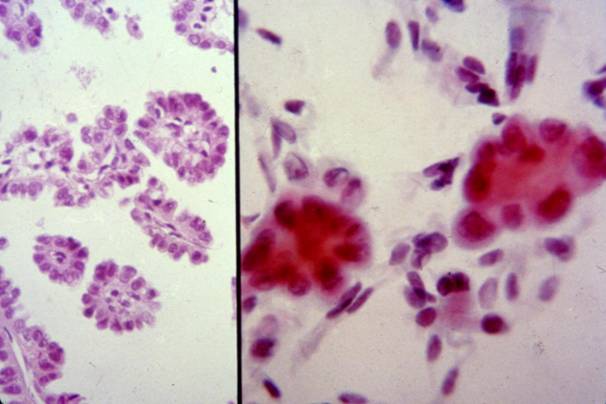
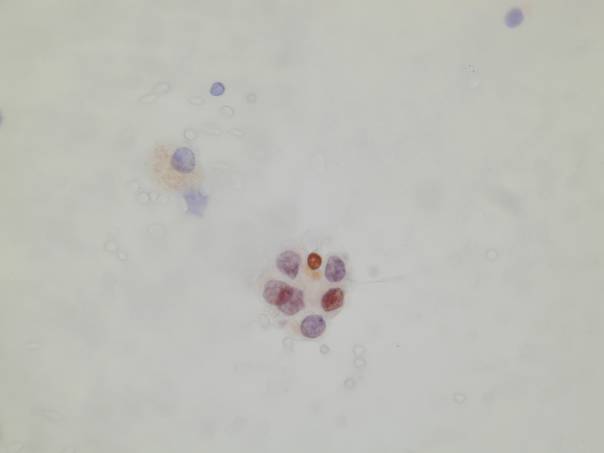
Cytologic diagnostic features (sputum and bronchial washing)
- Small glandular clusters
- Regular small cells with large cytoplasm
- Nuclear hyperchromasia or vescicular nuclei with prominent nucleoli
- Clean background
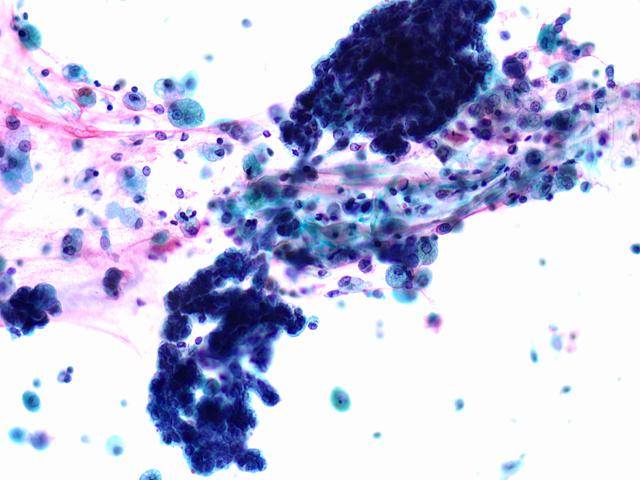
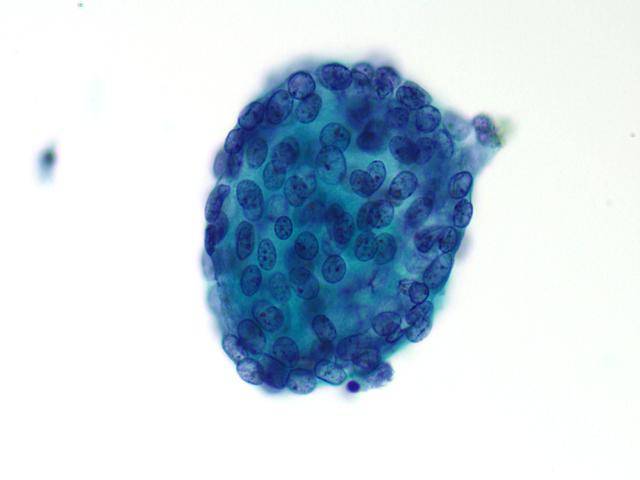
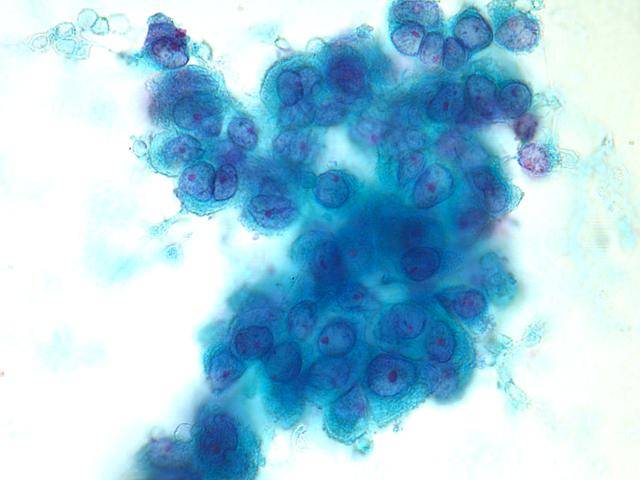
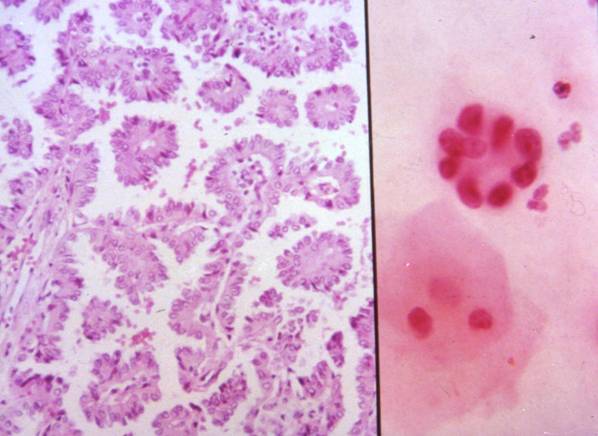
Cytologic diagnostic features (FNA and bronchial brushing)
- Monotonous cell population
- Arrangements in cellular balls, sheets and papillae
- Clean background
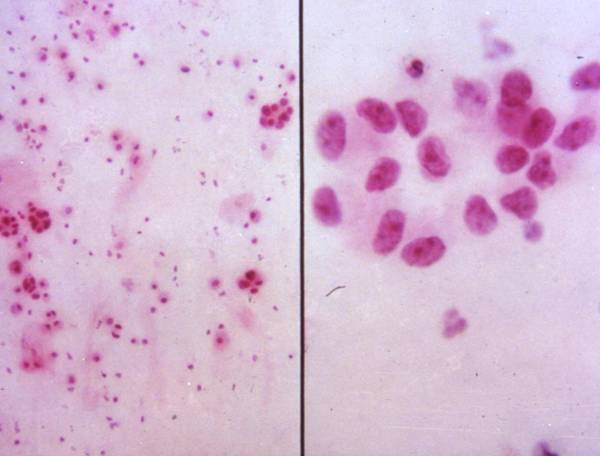
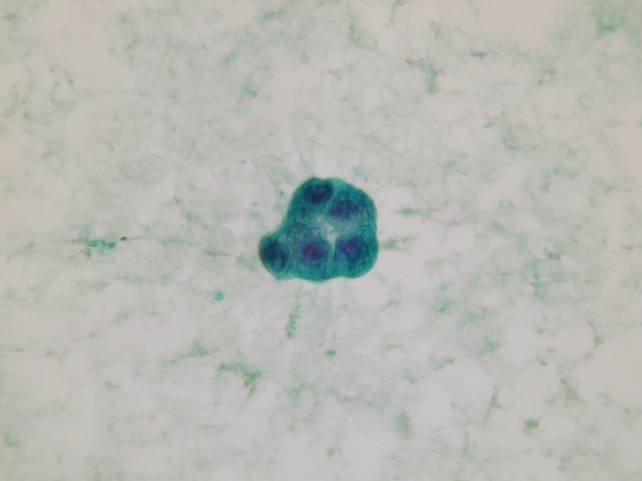
The bronchioloalveolar carcinoma can be hardly distinguished from classic adenocarcinoma on cytologic preparations. Some cases may strictly resemble a papillary thyroid carcinoma, because of the presence of psammoma bodies, occasional nuclear grooves and pseudoinclusions, optically clear nuclei. Clinical history is helpful to exclude a metastasis.
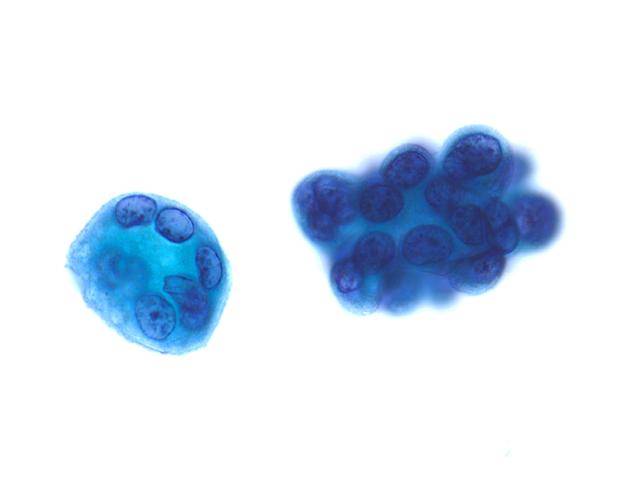
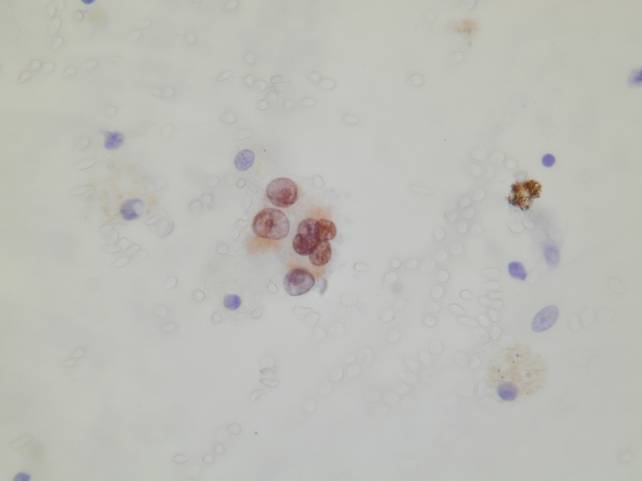
Immunocytochemistry
- Cytokeratin 7 +
- Cytokeratin 5 –
- Cytokeratin 20 –
- Neuroendocrine markers +-
- TTF-1 +
FNA of BAC - TTF-1