| Physiopathology of the effusions |
| Specimen collection and preparation methods |
| Accuracy |
| Reporting terminology |
| Benign elements |
| Non-neoplastic conditions |
| Malignant effusions |
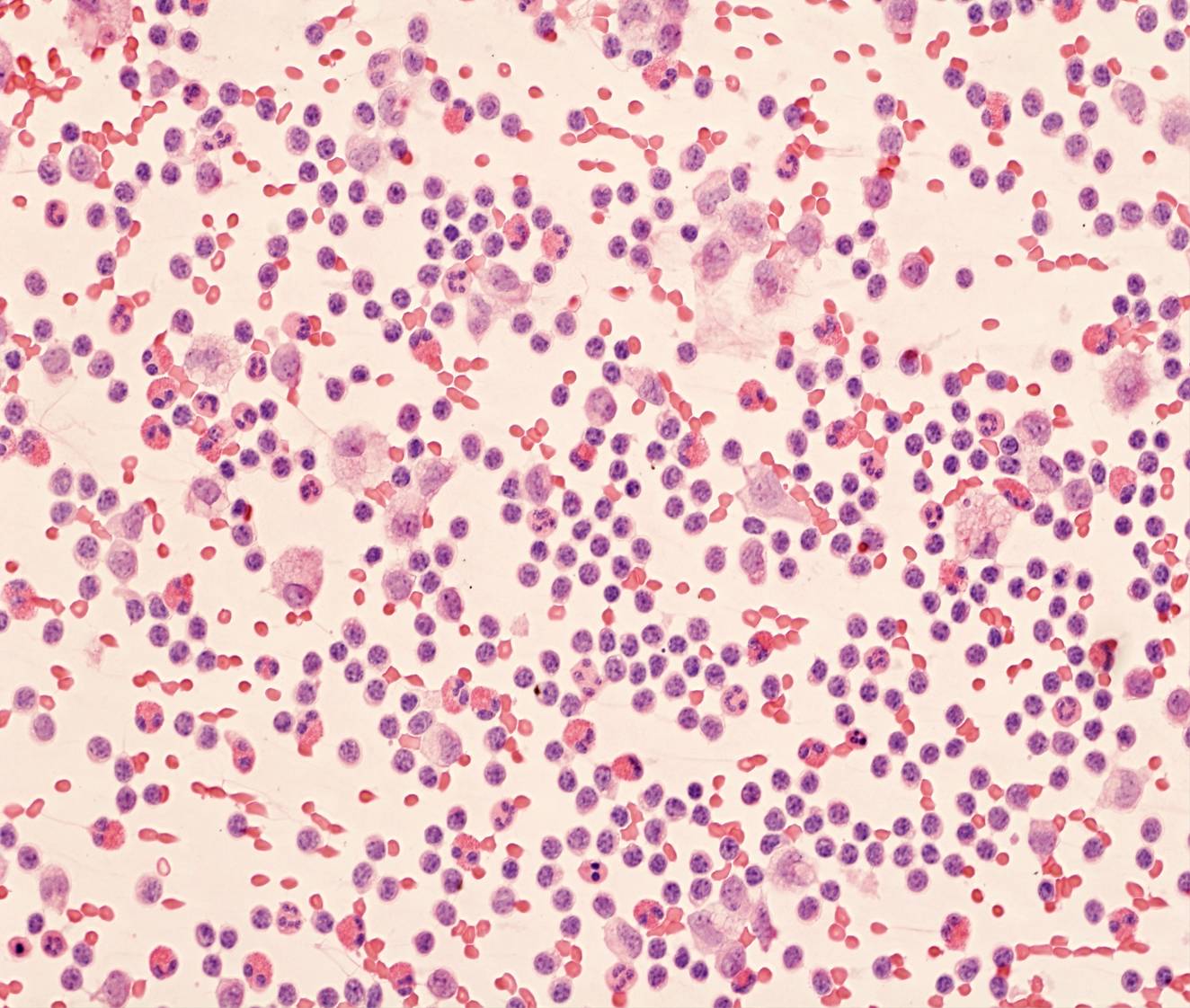
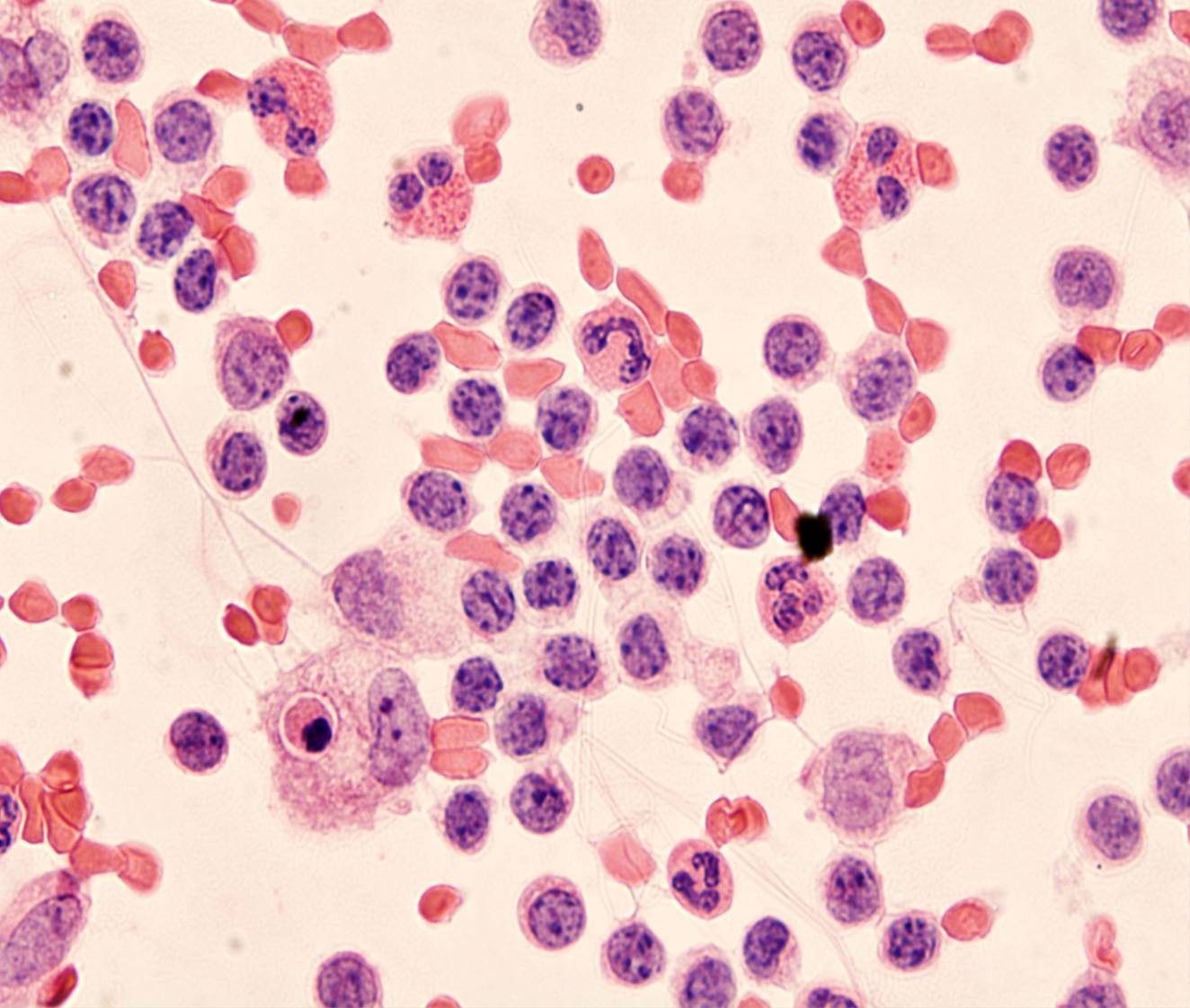
Tuberculosis pleuritis
- 80-100% lymphocytes
- No or few mesothelial cells
Pleural effusions in patients with tuberculous pleuritis have a characteristic, but not specific, cytologic appearance. The fluid is turbid and greenish-yellow. Cytologic preparations are highly cellular and composed almost exclusively of dispersed small lymphocytes, which immunophenotyping shows to be T cells. Mesothelial cells and histiocytes are either absent or present only in very small numbers.
The differential diagnosis includes non-tuberculous inflammatory effusions, which usually show a more polymorphous infiltrate with lymphocytes, neutrophils and histiocytes, as well as mesothelial cells.
Effusions caused by small lymphocytic lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic leukemia closely resemble tuberculous effusions; because these are B-cell neoplasms, immunocytochemistry and flow cytometry can be helpful.
Causes of increased lymphocytes in effusions
- Metastatic cancer
- Pulmonary tuberculosis
- Chronic inflammation
In these benign conditions lymphocytes are polyclonal, predominantly T cells. Differential diagnosis with CLL/SLL, where monoclonal, predominantly B cells are present.